Cybersecurity Controls Explained in Detail
-
 By Preetham Reddy
By Preetham Reddy
- Published on Feb 26 2025

Introduction to Cyber Security
Cybersecurity is a fast-growing industry in this era, where the main aim is to reduce cyberattacks. Cybersecurity professionals are responsible for protecting IT infrastructure and controlling devices, networks, and data. So what is cybersecurity? Why is it so important? What are the effective controls used to oppose cyberattacks? Let us learn in detail in this article.
Cybersecurity is a technique that protects internet-connected systems such as computers, servers, mobile devices, and networks from malicious activity. Cyber refers to technology that includes networks, programmes, systems, and data. And security refers to safeguarding all the above-mentioned cyber assets.
Cybersecurity is also called electronic information security or information technology security.
Table of Contents
Types of Cyber Security
Every organization wants to have an advantage when it comes to securing the systems and information. So the systems should contain strong security features that should keep the organization's data secure.
Therefore, cyber security provides the following domains:
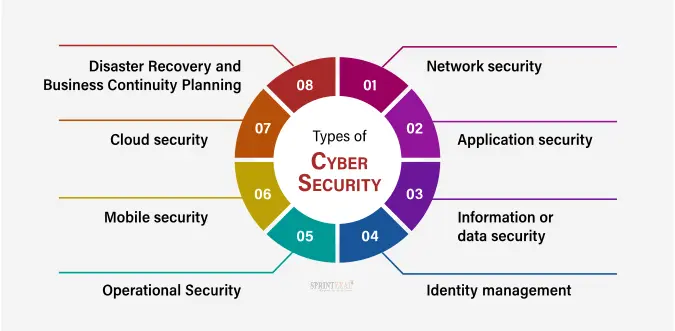
- Network security: It implements hardware and software devices in a system to secure its computer network from unauthorised entry, intruders, attacks, disruption, and misuse. Network security helps an organization protect its data from internal and external threats.
- Application security: It protects software and devices from unwanted threats. This security function can be used frequently by updating the apps and ensuring they are free from attacks. Effective security begins in the design stage, with the writing of source code, verification, threat modeling, etc. before deploying the program or a device.
- Information or data security: implementation of a strong data mechanism to maintain the integrity and privacy of data, both in storage and in transit, i.e., (in transformation)
- Identity management: It determines the level of access that each individual has within an organization.
- Operational Security: This cyber security type processes and makes decisions to handle data and secure resources.
- Mobile security: It secures the regular incoming and personal data stored on mobile devices.
- Cloud security: It protects the information stored in a digital environment or data in the cloud for the organization. Cloud security uses various service providers known as AWS, Azure, Google, etc., to verify security against multiple threats.
- Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity Planning: It reviews the monitoring process, alerts, and plans of an organization responding to any malicious activity causing loss of data or operations. This security deals with policies that instruct to resume lost operations after any disaster takes place to the same operating capacity as before the event.
The above-discussed types are essential to bringing cyber security to life.
Why is Cyber Security Important?
We live in a digital era where all of our lives revolve around the computer and other electronic devices. All of the critical infrastructures like a banking system, healthcare, financial institutions, governments, and manufacturing industries use internet-connected devices, to perform core operations.
Some of their important information, such as intellectual property, financial data, and personal data, can be sensitive. To protect that data from intruders and threat actors who would want financial gain, cyber security is implemented.
Cyber-attacks have now become an international concern because hacking, and all other security attacks will endanger the global economy. Hence, it is important to have an excellent cyber security strategy, to protect sensitive information from high-profile security breaches.
Governments around the world are paying more attention to cybercrimes. GDPR i.e. General data protection regulation is the best example of how changes are made in cyber security.
Cybersecurity contains essential security goals, which makes it more effective. Let us learn about cyber security goals in the following sections.
Cyber Security Goals
The main objective of cyber security is to ensure data protection. Cyber security offers three related principles to protect data from breaches; the principle is called the CIA triad. CIA can be broken into three parts,
- Confidentiality: It gives access to only authorized users, unauthorized users will be blocked. An example of this is Data encryption.
- Integrity: This principle makes sure that the data is authentic, accurate, and safeguarded from unauthorized modification or accidental user modification.
- Availability: Information will be made available only to authorized users. It ensures that malfunctions and cyberattacks are blocked to secure the system.
To secure data from malicious activities Cybersecurity contains essential controls, let us know in the following what it has to offer in detail.
Read more about cyber security and the best protocols used for cyber-attacks.
What is Cyber Security Control?
The controls are created to ensure the CIA triad i.e. confidentiality, integrity, and availability of an organization’s information and technology assets. And controls revolve around four essentials of people, technology, processes, and strategy.
Cyber security control is a mechanism that is used to prevent, detect and reduce cyber-attacks and threats. Cyber security controls are every organization's need, as it is used to manage the security program of a company/organization.
Cyber security is the top priority of organizations, where they determine what control they need. Here are some of the effective smaller controls used by every organization,
Update OS: when a threat or intrusion is found in the software, the technical staff try to work on it and will provide an updated version of the software. Keeping the system updated will help control the threats and security features will get better.
Granted applications: Meaning that a computer is configured to only run an application that is permitted by the organization. This control is hard to manage application in cyber security if done, there will be no cyber-attacks or data breaches taking place.
Reinforce system’s security: Being aware of the programmable settings in the OS i.e. operating system and applications are configured for security. And it is recommended to regularly re-install parts of the OS that will never be used.
Implement Multi-factor authentication: adding two-step verification is going to do good, to keep your data secure. The best example is Gmail, where you can set two-step verification so that no one can get into your mail details.
One of the most widely adopted approaches within multi-factor authentication is SMS OTP Verification, where a one-time password sent to a user’s mobile device adds an extra layer of identity assurance against unauthorized access.
Suggested Read: Get CISM certification and become a certified security manager.
Need for Cyber Security Controls
All systems contain weaknesses where some might be simple and some are complex. If a cyber attacker gets to know about the weak points in the system they will try to exploit it. Measures taken by an organization to stop these threats are known as security control.
Cyber security controls are the countermeasures taken up to reduce the chances of a data breach or system attack. The essential and tough work to do in cyber security is to select the right control, but most organizations do it wrong.
Cyber threats are automated and aimed at by cyber attackers. The attacks can be in the forms of malware, formjacking, Cryptojacking, Domain name system attacks, and in various ways they try to get into the system. It becomes a challenge to face all these, cyber security controls help to mitigate most of the threats.
For users on Apple devices, using anti malware for Mac adds an extra layer of defense against such evolving threats. Reducing the threats is always a need, errors that happen in the system can be controlled using essential cyber controls like,
- Applying antivirus solutions.
- Emphasize employee training and awareness
- Maintain secure portable devices
- Securely encrypt and backup data
Controls in cyber security contain different classes that split up the types of controls, which are considered based on their importance and classification.
Types of Cyber Security Controls
The essential cyber security controls are divided into three types, technical, administrative, and physical. The main goal of implementing security control is preventative, detective, corrective, compensatory, or deterrent. Let us understand each of them in the following,
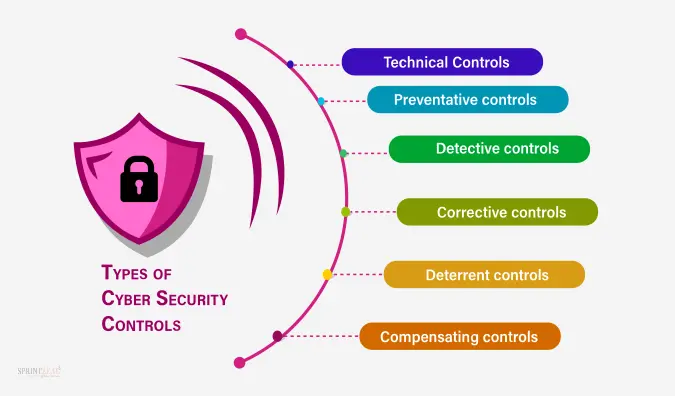
Technical Controls
Technical controls are also known as logical controls. That is used to reduce attacks on both hardware and software. And automated software tools are installed to protect the system.
In addition to these measures, tools like Multilogin can be employed to manage multiple browser profiles securely.
Examples of technical controls that are used to protect the system are as follows,
- Encryption
- Antivirus and anti-malware software
- Firewalls
- Security information and event management (SIEM)
- Instruction Detection Systems (IDS) and Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS)
Technical control is implemented using two methods,
Access Control Lists (ACL): ACL is a network traffic filter that controls incoming and outgoing traffic. They are commonly used in routers or firewalls, but they can also be programmed in any device that runs on the network, from hosts to servers.
Configuration Rules: It is a set of instructional codes used to guide the execution of the system when information is passed through it.
Administrative controls: Administrative security controls refer to policies, procedures, and guidelines that define the roles or business practices of an organisation’s security goals.
To implement administrative controls, additional security controls are necessary for monitoring and enforcement. The controls used to monitor and enforce them are as follows,
Management controls: This control is used to mainly focus on risk management and information security management.
Operational controls: The security controls that are primarily implemented, like technical and managerial controls executed by people, are saved by operational controls.
Physical controls: Physical security controls in cyber security are implemented based on cyber measures in a defined structure. That is used to detect or prevent unauthorized access to sensitive data.
Examples of physical controls are as follows:
- Closed-circuit surveillance cameras
- PoE camera systems
- Motion or thermal alarm systems
- Security guards and picture IDs
- Locked and dead-bolted steel doors
- Biometrics
Preventative controls
These controls are used to prevent loss or errors. Examples of preventative controls are as follows,
- Hardening: It’s a process of reducing attacks and tightening security controls.
- Security awareness training: is the process of providing formal cyber security education to employees and stakeholders about security threats and the organization's policies and procedures.
- Change management: Measures taken by an organization to describe and implement changes both internally and externally in the system that include preparing and supporting employees to take the necessary steps for change.
- Account disable policy: This policy will disable the account when an employee leaves the organization.
Detective controls
It is an accounting term, that uses internal control to find errors within the organization. Examples of detective controls are as follows:
- Log monitoring – analyzing real-time data.
- SIEM- A set of tools and services are offered to analyze various system operational logs.
- Trend Analysis – Identifying the pattern from an application’s log output, to gather relevant information.
- Security Audits- set of measures that focus on cyber security standards and guidelines.
- Video Surveillance - Digital images and videos that are sent over communication networks are monitored.
- Motion Detection – Sensors are attached to detect nearby motions.
Corrective controls
After a system malfunction, corrective controls are used to make the system more effective to use. Examples of corrective controls include,
- IPS: detection of anomalies in traffic flow to quickly prevent malicious activity.
- Backups and system recovery: the Process of creating and storing data copies that can be used as backups when data is lost.
Deterrent controls
Deterrent controls are used to reduce deliberate attacks, which are usually in the form of a tangible object or person. Examples of deterrent controls include
- Cable locks
- Hardware locks
- Video surveillance and guards
Compensating controls
Compensating control is an alternative method that is used to satisfy the requirement for security. And certain security measures can’t be implemented due to financial or simple impractical reasons at the time.
Example of Compensating control,
Time-based OTP- One of the best examples for compensating control is OTP, i.e., One-time password, where a code is generated by an algorithm that uses the current time of day as one of its authentication factors.
Cyber Security Risks and Controls
The digital world of today offers many cyber threats to which businesses must defend themselves against from data integrity to financial stability and operational resilience. Cyber Security Controls must be enforced on the digital assets at organization level to mitigate changing risks. Cyber security risks are the most important of the following
Malware Attacks –Viruses, worms and ransomwares are just some of the malware which can infiltrate systems and siphon sensitive data.
- Phishing Scams – Fraud Emails And Message Penetrate the User into Filling of Confidential Info
- Insider Threats – Employees or contractors with access to sensitive information may pose security risks.
- DDoS Attacks – Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks overwhelm systems, rendering them inoperable.
- Data Breaches – Unauthorized access to confidential information can result in financial and reputational damage.
- Zero-Day Exploits – Attackers exploit vulnerabilities before a fix is available, making early detection crucial.

To mitigate these risks, organizations must implement strong Cyber Security Controls, which include:
- Network Security Measures – Firewalls, intrusion detection/prevention systems, and secure network configurations.
- Access Management – Role-based access control (RBAC), multi-factor authentication (MFA), and strong password policies.
- Data Protection Strategies – Encryption, regular backups, and secure storage mechanisms.
- Security Awareness Training – Educating employees about cyber threats, phishing scams, and safe browsing habits.
- Incident Response Plans – Establishing protocols for detecting, reporting, and mitigating cyber incidents.
By adopting a proactive approach, organizations can minimize vulnerabilities and strengthen their cyber defense mechanisms.
Cybersecurity Controls Assessment
Assessing Cyber Security Controls is a critical process to ensure the effectiveness of an organization's security framework. A well-structured assessment helps identify weaknesses, improve security posture, and comply with industry regulations.
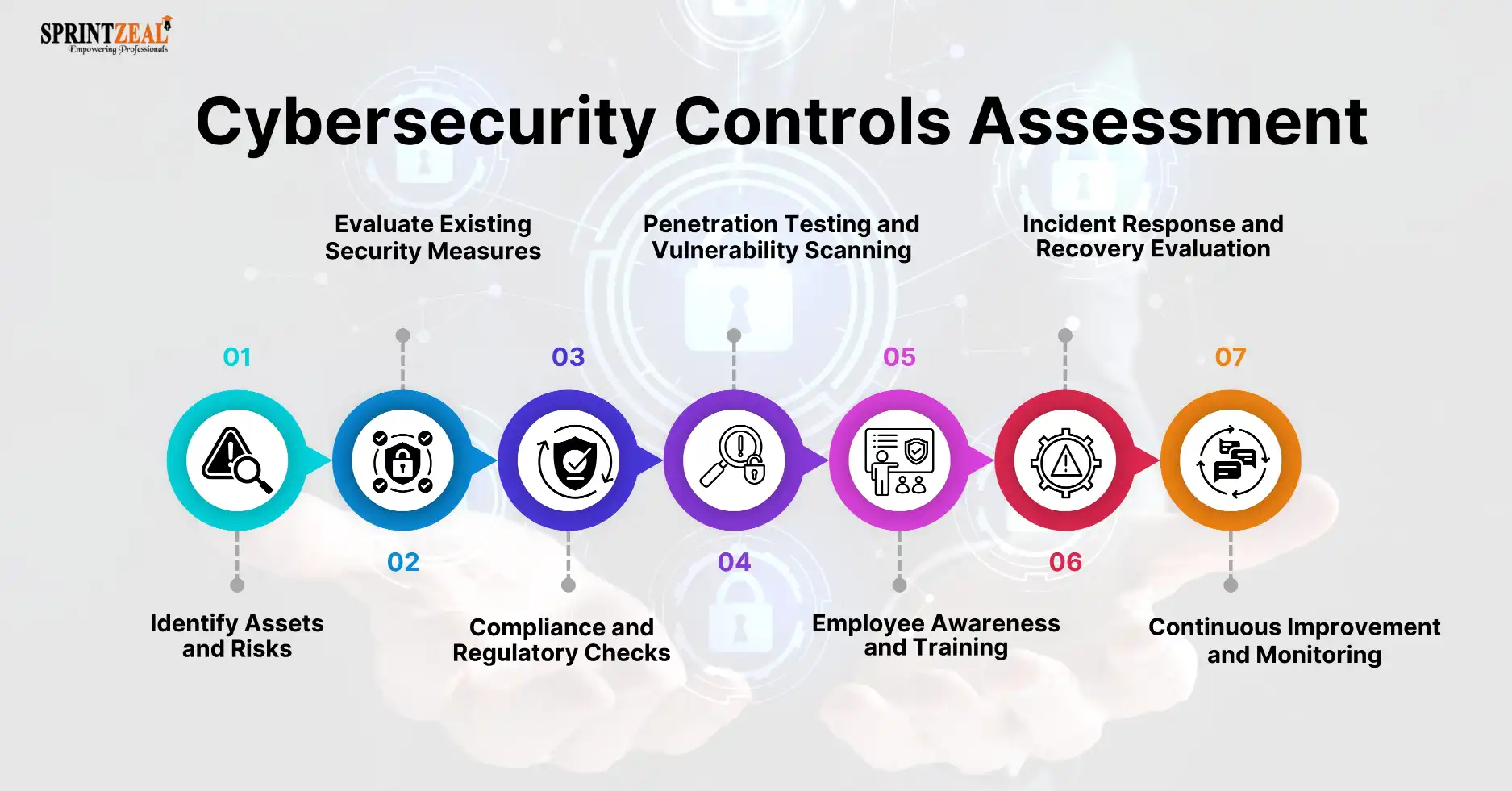
Key Steps in Cybersecurity Controls Assessment:
1) Identify Assets and Risks
Inventory all digital assets, including hardware, software, and sensitive data.
Conduct a risk assessment to understand potential threats and vulnerabilities.
2) Evaluate Existing Security Measures
Review firewalls, encryption protocols, access controls, and endpoint security solutions.
Analyze log monitoring and security audit reports for anomalies.
3) Compliance and Regulatory Checks
Ensure compliance with GDPR, HIPAA, ISO 27001, and other relevant standards.
Implement security policies that align with industry best practices.
4) Penetration Testing and Vulnerability Scanning
Conduct simulated attacks to test the resilience of security controls.
Use automated tools to scan for vulnerabilities in networks and applications.
5) Employee Awareness and Training
Assess the effectiveness of security awareness programs.
Conduct phishing simulations and cyber hygiene training sessions.
6) Incident Response and Recovery Evaluation
Review the organization's ability to detect, respond to, and recover from cyber incidents.
Update incident response plans based on new threats and lessons learned.
7) Continuous Improvement and Monitoring
Regularly update security policies and controls to address emerging threats.
Leverage threat intelligence and real-time monitoring tools for proactive security management.
By conducting a thorough Cyber Security Controls assessment, organizations can enhance their security infrastructure and ensure continuous protection against cyber threats.
Conclusion
Cyber security is one of the important aspects of the growing world. Threats are hard to deny and overcoming them is also a difficult task. But there is a need to learn how to defend them and also to manage the security activities of organizations and individuals. That could be done by using proper security controls. Monitor the valuable assets and keep your organization away from cyber threats.
Learn more about networking and security with our industry-level all courses and get certified by ISC2 through Sprintzeal. Contact us for further course details or email us, subscribe to our newsletters.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are controls in cyber security?
Cyber security controls are measures put in place to protect digital systems, networks, and data from cyber threats. These controls help organizations prevent, detect, and respond to security risks effectively. Examples include firewalls, encryption, multi-factor authentication, and security awareness training.
What are the 5 basic security controls?
The five basic security controls that every organization should implement are:
- Firewalls – Protect networks from unauthorized access.
- SaaS access controls – Restricts data and system access to authorized users only.
- Antivirus & Malware Protection – Detects and removes malicious software.
- Data Encryption – Secures sensitive data by converting it into unreadable formats.
- Security Awareness Training – Educates employees on best practices to avoid cyber threats.
What are the 4 types of security controls?
There are four main types of cyber security controls:
- Preventive Controls – Aim to stop attacks before they happen (e.g., firewalls, access controls, security policies).
- Detective Controls – Identify and alert on security breaches (e.g., intrusion detection systems, log monitoring, antivirus software).
- Corrective Controls – Help recover from security incidents (e.g., data backups, incident response plans, patch management).
- Deterrent Controls – Discourage cyber attacks by imposing consequences (e.g., security policies, legal actions, penalties).
Popular Programs
CISSP® - Certified Information System Security Professional
Live Virtual Training
- 4.8 (964 + Ratings)
- 50k + Learners
CISM® - Certified Information Security Manager
Live Virtual Training
- 4.3 (200 + Ratings)
- 11k + Learners
CCSP® - Certified Cloud Security Professional
Live Virtual Training
- 4.3 (964 + Ratings)
- 19k + Learners
Trending Posts
What is Cybercrime? Exploring Types, Examples, and Prevention
Last updated on Jul 24 2023
What is OSI Model? - Layers of OSI Model
Last updated on Jan 16 2026
Information Assurance Careers - Exploring Career Paths
Last updated on May 25 2023
Top 10 Network Scanning Tools of 2026
Last updated on Oct 29 2025
IBM Data Breach: Is IBM Really Breach-Proof?
Last updated on Dec 3 2024
What is Digital Forensics? Types, Process & Challenges
Last updated on Jun 5 2023
Categories
- Other 88
- Agile Management 48
- Cloud Computing 58
- Project Management 175
- Data Science 71
- Business Management 89
- Digital Marketing 89
- IT Service Management 36
- Programming Language 61
- AI and Machine Learning 94
- IT Security 113
- Quality Management 78
- IT Hardware and Networking 28
- Microsoft Program 5
- Workplace Skill Building 15
- Risk Management 10
- Information Security 8
- Leadership and Management 10
- Corporate Training and Development 1
Trending Now
Top 5 Compelling Reasons To Get A Cyber Security Certification
ebookHow to Become IT Security Expert with CISSP Certification
ebookTop 20 Reasons You Should Get a CISSP Certification
ebookWhat is CISSP? – Everything about CISSP Certification Explained
ebookPass CISSP Exam - How to Clear CISSP Exam in First Attempt 2026 (UPDATED)
ebookCISSP Certification – Top 25 Career Benefits in 2026
ebookCybersecurity – Everything You Need to Know About it
ebookUpdated Google Certification Training Course list 2026
ArticleWhich Certification is best for Cybersecurity?
ebookWhich Cybersecurity Certification Should I Get First?
ebookCysa+ certification – Should you get it?
ebookList of Top Security Certifications
ArticleEasiest Security Certification to Get
ebookCISM certification cost and career benefits
ebookCybersecurity Fundamentals Explained
ebookISACA Certifications List 2026
ebookCareer Benefits of CISM Certification in 2026
ArticleList of Top Information Security Certifications in 2026
ebookCISM certification cost details
ArticleMitigate the Cyber-Attack Risks with Best Cyber Security Protocols
ebookCybersecurity Interview Questions and Answers 2026
ebookTop Cybersecurity Software Tools In 2026
ebookInformation Security Analyst - Career, Job Role, and Top Certifications
ebookCyber Security Analyst - How to Become, Job Demand and Top Certifications
ebookWhat is Data Security - Types, Strategy, Compliance and Regulations
ebookData loss Prevention in Cyber Security Explained
ebookCybersecurity Framework - A Complete Guide
ebookWhat is Cryptography - A Comprehensive Guide
ebookData Leak - What is it, Prevention and Solutions
ebookCybersecurity Career Paths Guide
ebookFuture of Cybersecurity - Trends and Scope
ebookCyber Security Careers and Outlook - 2026 Guide
ebook5 Cybersecurity Predictions in 2026 - Trends and Challenges
ebookScope for Cybersecurity in 2026 - Latest Update
ebookEthical Hacking Career: A Career Guide for Ethical Hacker
ebookApplication Security: All You Need To Know
ebookCybersecurity Roles - Top Roles and Skills to Consider in 2026
ebookHow to Get Cyber Essentials Certified
ebookTop 10 Cyber Security Threats and How to Prevent Them
ebookTop 10 Network Scanning Tools of 2026
ebookCyber Incident Response Plan: A Comprehensive Guide
ebookInformation Assurance Careers - Exploring Career Paths
ebookWhat is the Department of Defense (DoD) Directive 8140
ebookCybersecurity Mesh Architecture: What It Is and How to Build It
ebookWhat is Threat Modeling? Methodologies, Types, and Steps
ebookWhat is Digital Forensics? Types, Process & Challenges
ebookInformation Assurance Model in Cybersecurity
ebookHow to Become an Information Security Analyst Salary, Skills, and More
ArticleList of Top Department of Defense (DoD) Approved 8570 Certification Courses
ebookTop 5 Ransomware Attacks to Watch Out for in 2026
ebookJob Prospects for DoD Certified Professionals: A Pathway to Success in cybersecurity
ebook10 Biggest Data Breaches of the 21st Century
ebookWhat is a Cybersecurity Incident?-Types, Impact, Response Process and More
ebookCyber Security Planning - A Detailed Guide for Risk Mitigation
ebookWhat is Cybercrime? Exploring Types, Examples, and Prevention
ebookRecent Cyber Attacks & Data Breaches in 2026
ebookCybersecurity Strategy: Building a Strong Defense for Business
ebookCybercrime Impacts On Business: 6 Major Effects
ebook5 Types of Cyber Attacks You Should Be Aware of in 2026
ebookCloud Cyber Attacks: Causes, Types, Prevention and Protection
ebookCloud Malware: Types of Attacks and Security Measure
ebookCyber Attack Statistics and Trends to Know in 2026
ebookList Of Top Cybersecurity Threats In 2026
ebookSafeguarding Digital Domain: 10 Most Common Cybercrimes
ebookDemystifying Cloud-Based Cyber Attacks: A Comprehensive Guide
ebookPrevent Cyber Attacks: Strategies to Protect Your Digital Assets
ebookList of Top 10 Cybersecurity Careers in 2026
ebookTop 20 Cybersecurity Trends to Watch Out for in 2026
ArticleHow to Become Cybersecurity Engineer
ArticleUnderstanding Risk assessment in audit planning
ArticleFundamentals of Risk-Based Auditing: A Strategic Framework
ArticleRisk-based Audit Planning Guide for Beginners
ebookTop 8 Types of Cybersecurity Jobs and Salary Insights
ArticleA Comprehensive Guide to Building Risk-Based Internal Audit Plan
ArticleRisk-Based Internal Auditing Approaches: 7 Steps to Explore
ArticleCompTIA Security+ 601 vs. 701: Understanding Key Differences
ArticleWhy and How to Perform a Risk-Based Internal Audit
ArticleRisk-Based Auditing Techniques Explained
ebookEvolving Cyber Threats and Vulnerabilities in Cybersecurity Risk Management
ArticleWhat Is Secure Access Service Edge (SASE)?
ArticleHow to Stay Cyber-Secure in Work and Personal Life (Tips and Practices)
ArticleIBM Data Breach: Is IBM Really Breach-Proof?
ArticleTarget Cyber Attack: Key Lessons from the 2013 Data Breach
ArticleLinkedIn User Data Protection Explained
ArticleCanva Data Breach: Best Lessons for Users and Businesses
ArticleHow Did Capital One Respond to Their Major Cyber Incident?
ArticleWhat Innovative Measures Did Reddit Take to Protect User Data?
ArticleHow Does Slack Respond to Security Challenges?
ArticleTwitch Data Breach: Response, Changes, and Key Takeaways
ArticleGuess What Google Did When a Employee Breached Their Firmware
ArticleEthical Hacking Tools: Best Ones for Cybersecurity in 2026
ArticleWhat Happened When Cisco Faced a Cyber Incident?
ArticleWhat Sony Did to Rebuild Trust After a Major Cyberattack
ArticleHow to Handle a Data Breach? Learn from Microsoft!
ArticleCybersecurity Mesh: A New Approach for Security Design
ArticleHow Target Turned a Cyber Crisis into a Lesson for All
ArticleDropbox Data Breach: What Companies Can Learn from It
ArticleHow JPMorgan Chase Strengthened Security After Facing Cyber Threats
ArticleThe Future of Online Security: Trends to Watch in 2026
ArticleLatest Trends in CyberSecurity
ArticleTop 12 Cyber Security Apprenticeships with High Earning Potential in 2026
ArticleEnhancing Safety and Competence in Today's Workplace
ArticlePrivacy at Your Fingertips: How iPhone Users Can Use Tools Securely
ArticleAge Matters: Understanding the Generational Gap in Online Safety Education
ArticleCybersecurity 101: Why Cybersecurity is the Hottest Career Right Now
ArticleWhy Cybersecurity Training Should Be Part of Every Professional's Career Plan
ArticleHow to Protect Your Data When Traveling to Countries Like Malaysia?
ArticleTop Online Master's in Cybersecurity Programs for Working Professionals
ArticleHow AI Detectors Strengthen Cybersecurity in Modern Networks
ArticleHow to Become a Cybersecurity Engineer: Step-by-Step Career Guide
ArticleWhy Certification in Risk and Compliance Is Critical in Today’s Financial World
ArticleWhat is OSI Model? - Layers of OSI Model
Article



















