DMAIC vs. DMADV: Key Differences and Choosing the Right Six Sigma Methodology
-
 By Niharika Chaurasia
By Niharika Chaurasia
- Published on Nov 10 2023
Table of Contents
Six Sigma Methodology
In the world of improving how things work, there's a powerful tool called Six Sigma. It's like a super-skill for making processes better. Imagine it as your secret weapon for improving quality and efficiency in different tasks.
But here's the catch: Six Sigma has two main methods, like two sides of the same coin. These methods are called DMAIC and DMADV. Both DMAIC and DMADV share similarities, yet they also have distinct characteristics. The crucial question is determining when to employ each methodology. This is the aspect we will delve into in this blog.
Before we delve into contrasting DMAIC and DMADV, it's essential to understand the significance of Six Sigma.
Imagine you have a toolbox for making things work better, faster, and with fewer mistakes. In this world of striving for excellence, think of Six Sigma as your guide. It helps you discover and resolve issues, pointing you in the right direction. Now, consider DMAIC and DMADV as two distinct tools in that toolbox.
Both are useful, but it's essential to know when to apply each one. DMAIC is like a trusty wrench, perfect for fixing things that are a bit broken. On the other hand, DMADV is like a shiny new hammer, great for building something completely new and awesome.
In this blog post, we'll explain when to use DMAIC (the wrench) and when to go for DMADV (the hammer) to handle your projects effectively. Let's begin!
Understanding DMAIC
In the realm of Six Sigma, DMAIC is a potent method employed for enhancements. But what does it entail, and how does it function? Let's explore further.
DMAIC stands for five important steps: Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control. It's a roadmap that guides us to improve a process.
The first step, "Define," sets the stage. In this phase, we clearly describe the problem or goal. Think of it as the "what" and "why" part of the process. Now, let's look at the key components of DMAIC:
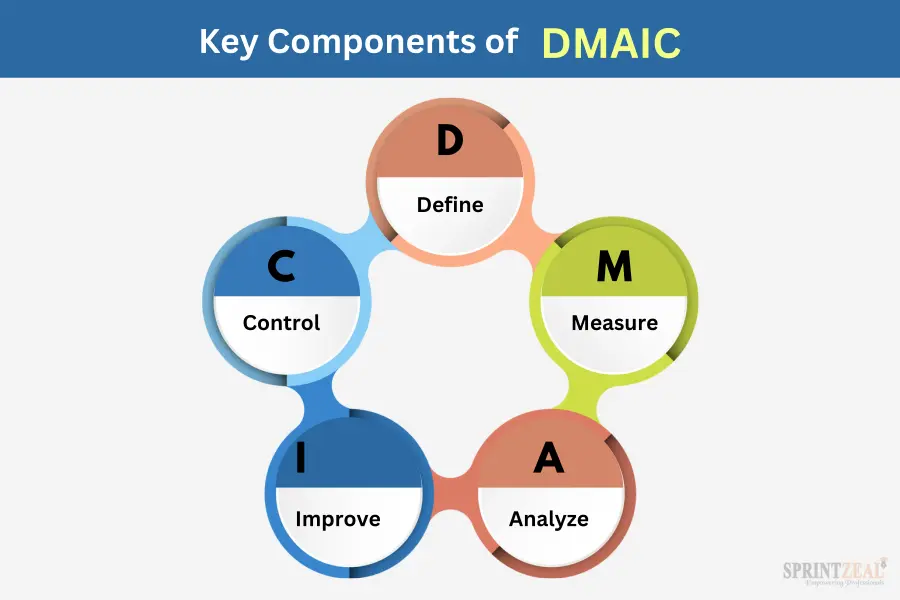
- Define: In this phase, you figure out what needs fixing or improving. You set specific goals and identify the people involved.
- Measure: Once you know what to improve, it's time to measure how things are currently working. This involves collecting data and understanding the process's current state.
- Analyze: After collecting data, you analyze it. This helps you find the root causes of any problems. It's like detective work for processes.
- Improve: With a good understanding of what's wrong, you can start making changes. This phase is all about finding solutions and putting them into action.
- Control: The last step ensures that the improvements stick around. You put measures in place to keep things on the right track.
When to Use DMAIC
Picture yourself working at a bakery, and you've observed that the cookies frequently turn out somewhat varied in size, color, and flavor. This lack of consistency is an issue, and you aim to resolve it. DMAIC can help.
You would define the issue (inconsistent cookies), measure how different they are, analyze the causes (like variations in the oven temperature), implement changes in your baking process, and control the new process to make sure the cookies come out consistently delicious. In this section, we'll explore the DMADV methodology within the Six Sigma framework. We'll break it down step by step and discuss what DMADV is all about.
Understanding DMADV
DMADV stands for Define, Measure, Analyze, Design, and Verify. It's a structured approach used in Six Sigma for creating brand-new processes, products, or services. Unlike DMAIC, which focuses on improving existing processes, DMADV is all about starting from scratch to build something new and better.
Key components of DMADV:
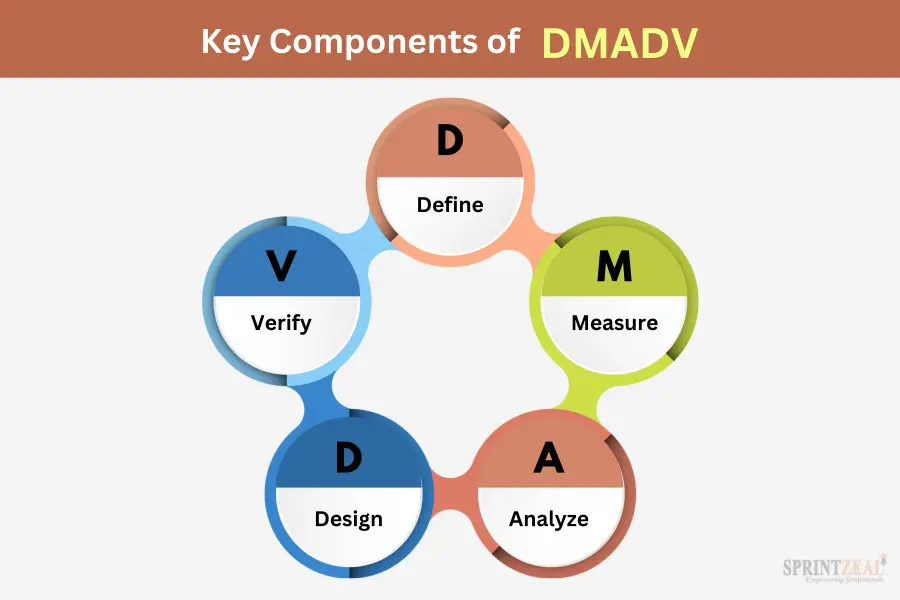
- Define: To begin, you should start by making a clear plan for what you want to make. This involves setting clear goals, knowing what your customers want, and recognizing any limits that could impact your project.
- Measure: After defining your project, you'll gather data to measure the current state. This helps you understand where you're starting from and what needs to be improved.
- Analyze: In the Analyze phase, you dig deeper into the data you've collected. You look for patterns, trends, and possible issues that might come up during the design phase. This step ensures you're well-prepared to tackle any challenges.
- Design: The heart of DMADV is the Design phase. This is where you create your new process, product, or service. It involves brainstorming, planning, and making decisions about how things will work in the future.
- Verify: Once your new design is ready, you need to make sure it meets the needs of your customers and works as intended. The Verify phase is like a final check to ensure your creation is up to the mark.
When to use DMADV
DMADV is ideal for projects where you need to invent something entirely new. Here are some examples:
New Product Development: If your company is designing a brand-new product that hasn't existed before, DMADV is the way to go. This could be anything from a new smartphone to a revolutionary medical device.
Process Innovation: When you're trying to create a more efficient process or a new way of doing things, DMADV can help. For instance, a car manufacturer might use DMADV to develop a more eco-friendly assembly line.
Service Improvement: Even in the service industry, DMADV can be applied. Let's say a hotel wants to completely overhaul its check-in process to make it faster and more customer-friendly. DMADV is the go-to choice.
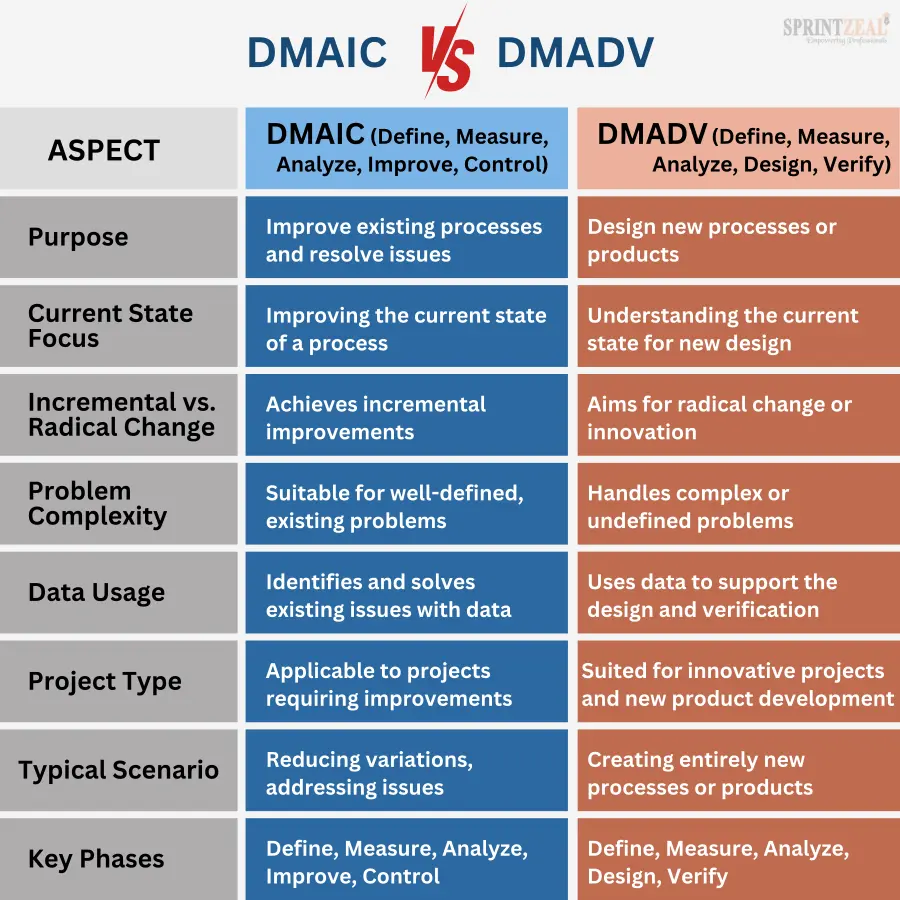
DMAIC vs DMADV - What are the Differences?
In this section, we will explore the significant differences between the DMAIC and DMADV methodologies within the Six Sigma framework. Understanding DMAIC vs DMADV is crucial for making the right choice when improving your processes.
- Phases and Objectives
DMAIC: The DMAIC methodology, which stands for Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control, is primarily used for process improvement. Its main objective is to identify and address existing issues within a process. The phases in DMAIC are designed to help you understand, analyze, and improve the current state of a process, ultimately leading to better control and consistency.
DMADV: On the other hand, DMADV, short for Define, Measure, Analyze, Design, and Verify, is focused on creating something new or redesigning existing processes. Its primary objective is innovation and the development of entirely new processes or products. In DMADV, you start with the existing state but focus on designing a future state that is better, more efficient, and aligned with customer requirements.
- Project Types and Scenarios
DMAIC: DMAIC is the go-to methodology when you're dealing with well-defined problems or when the issues in a process are clear and measurable. It's best suited for situations where incremental improvements are sufficient to meet your project objectives. DMAIC works wonders in scenarios where you want to reduce variations in the process, making it more consistent and reliable.
DMADV: DMADV comes into play when you're dealing with complex or undefined problems. This is the top choice when you aim to be imaginative, create something entirely fresh, or bring substantial alterations to existing procedures or items. DMADV is your preferred method for projects that require imaginative solutions and thinking outside the box to fulfill customer needs.
- Approach to Data
DMAIC: In DMAIC, we use data to understand what's happening with our current process. It's similar to how we use a magnifying glass to investigate problems. We examine data to identify issues and come up with solutions.
DMADV: However, uses data in a distinct manner. It aids in crafting something fresh and intriguing. Think of it as using a compass to chart a new course. DMADV utilizes data to craft a roadmap for the future, making sure that the upcoming process or product aligns with what the customer wants.
- Focus on Innovation
DMAIC: This method is like a doctor who diagnoses and treats an illness. It's about finding and curing existing problems. DMAIC doesn't focus on creating new solutions or innovations; its goal is to restore health to the existing process.
DMADV: DMADV is like an artist who starts with a blank canvas and paints a masterpiece. It's all about innovation and creativity. When you use DMADV, you're aiming to design something entirely new and exciting. This could be a new product, service, or process that no one has seen before.
- Complexity of the Problem
DMAIC: If the problem you're facing is like a puzzle with missing pieces, DMAIC is your friend. It's great for dealing with issues that are well-defined and not too complex.
DMADV: If you're facing a complex problem that's as tricky as a maze, full of twists, turns, and many uncertainties, DMADV can be your guide. It's perfect for intricate problems where you must create a clear route from the beginning to the end.
- Resource Requirements
DMAIC: This method is generally less resource-intensive. Think of it as employing the tools you already possess in your toolkit to repair something. You might not require many extra resources or advanced gear.
DMADV: DMADV can be more resource-heavy. When you're making something brand-new, it can require extra time, funds, and specialized tools to turn your creative ideas into reality.
By grasping these extra distinctions, you'll be better prepared to pick the suitable method for the task, whether it's enhancing procedures or crafting innovative products.
In essence, DMAIC and DMADV are like two powerful tools in your process improvement toolbox. You can use them individually based on your project's needs, or you can use them sequentially to first fix what's broken and then innovate for the future.
Understanding DMAIC vs DMADV is crucial in making informed decisions when choosing the right Six Sigma methodology for your specific project.
Pros and Cons of Each Methodology
DMAIC:
Pros:
- Well-suited for addressing known problems.
- Provides a structured approach to problem-solving.
- Enhances process stability and reduces variations.
- Easily integrated into existing processes.
Cons:
- May not be suitable for complex, innovative projects.
- Less effective for creating entirely new processes or products.
DMADV:
Pros:
- Ideal for innovative projects and new product development.
- Emphasizes customer requirements and innovation.
- Suitable for tackling complex, undefined issues.
- Allows for creative, out-of-the-box thinking.
Cons:
- Time-consuming, as it involves designing new solutions.
- May require more resources and investment.
- Tools Used by DMAIC and DMADV
Tools Used by DMAIC and DMADV
In the world of Six Sigma methodologies, both DMAIC and DMADV have a powerful arsenal of tools at their disposal. These tools are essential for collecting data, analyzing processes, and making informed decisions. Let's explore the key tools used by each methodology.
Tools Used by DMAIC:
Process Maps: Process maps are visual representations of a process that help in identifying inefficiencies and areas for improvement. They provide a clear picture of how a process works.
Cause-and-Effect Diagram (Ishikawa or Fishbone Diagram): This tool helps identify the root causes of problems. It's a visual representation that breaks down a problem into its potential causes, categorized into branches.
Data Collection and Analysis: DMAIC heavily relies on data collection and analysis. Tools such as histograms, control charts, and Pareto charts help in quantifying variations and making data-driven decisions.
Root Cause Analysis: Techniques like the 5 Whys and Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) are used to delve deep into problems and find their underlying causes.
Process Capability Analysis: Tools like Cp, Cpk, Pp, and Ppk are employed to assess the capability of a process to meet customer requirements.
Statistical Process Control (SPC): SPC tools, including control charts and run charts, are vital for monitoring and maintaining process stability.
Design of Experiments (DOE): DOE helps optimize processes by systematically testing multiple variables to determine their impact on the final outcome.
Tools Used by DMADV:
Quality Function Deployment (QFD): QFD is a tool used to translate customer requirements into specific product or process features. It ensures that the design aligns with customer needs.
Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA): While also used in DMAIC, FMEA plays a crucial role in DMADV to identify potential failure modes in a new design and prioritize them.
TRIZ (Theory of Inventive Problem Solving): TRIZ is a systematic approach for creative problem-solving and innovation. It encourages innovative thinking and inventive solutions.
Pugh Matrix: This tool is used to compare and evaluate multiple design concepts and select the most promising one.
Simulation: Simulation software allows for the virtual testing of a new process or product design. It helps in understanding how the design will perform in real-world conditions.
Design for Six Sigma (DFSS) Scorecards: DFSS scorecards provide a structured approach to evaluating the success of a new design in meeting customer requirements.
Axiomatic Design: Axiomatic design principles help in ensuring that the design aligns with customer needs and minimizes the complexity of the design.
It's important to note that both DMAIC and DMADV methodologies can use common tools, such as statistical software, process flowcharts, and brainstorming sessions. However, the emphasis and application of these tools differ based on the methodology's objectives.
Learn with Sprintzeal
Sprintzeal is your go-to destination for mastering Six Sigma methodologies, including DMAIC and DMADV. If you're looking to enhance your process improvement skills and gain valuable certifications, Sprintzeal offers comprehensive courses designed to fit your learning needs.
- Six Sigma Green Belt: Ideal for those looking to play a key role in process improvement and problem-solving within an organization.
- Six Sigma Black Belt: For those aiming to become experts in Six Sigma methodologies and lead complex projects.
- Lean Six Sigma Green Belt: Combines the principles of Lean and Six Sigma to optimize processes and reduce waste.
- Lean Six Sigma Black Belt: A comprehensive program that covers Lean and Six Sigma tools for process improvement and innovation.
If you're ready to take your process improvement skills to the next level and become a certified Six Sigma professional, look no further. Explore our courses, gain valuable insights, and make a significant impact on your projects and organization's success.
Visit Sprintzeal's website and take the first step towards becoming a Six Sigma expert. Join our courses, gain certifications, and unlock exciting opportunities for process improvement in your career!
Conclusion
In conclusion, we've explored the world of Six Sigma methodologies, specifically focusing on DMAIC and DMADV. Understanding DMAIC vs DMADV play a vital role in process improvement, and choosing the right one for your project is a crucial decision.
The importance of selecting the right Six Sigma methodology cannot be overstated. Making the right choice can be the difference between success and stumbling. Take your project objectives, complexity, available resources, and the level of innovation required into careful consideration before deciding which methodology is the best fit.
If you're looking to further expand your knowledge in Six Sigma and its methodologies, we recommend exploring the courses offered by SprintZeal. They provide in-depth training and certification opportunities, equipping you with the skills and expertise needed for effective process improvement.
Don't hesitate to take the next step in your Six Sigma journey. Visit SprintZeal's website and discover the courses that can propel your career forward.
FAQs
What is the difference in measure phase of DMAIC and DMADV?
The Measure phase in DMAIC focuses on collecting data to understand the current state of an existing process, while in DMADV, it is geared towards establishing a baseline for designing a new process or product.
What is DMADV methodology?
DMADV, which stands for Define, Measure, Analyze, Design, Verify, is a Six Sigma methodology primarily used for creating entirely new processes or products.
When should DMADV be used?
DMADV should be used when you're seeking to innovate, design new processes or products, and address complex, undefined issues.
What are the implications of DMAIC and DMADV?
The implications of DMAIC include improved process stability, waste reduction, and incremental enhancements, while DMADV leads to radical changes and innovations, potentially revolutionizing the way a process or product is designed or delivered.
Popular Programs
Trending Posts
Step-by-Step Implementation Guide to ISO 9001
Last updated on Jul 11 2024
Quality Manager Interview Questions and Answers for 2026
Last updated on Dec 8 2025
Six Sigma tools for DMAIC Phases
Last updated on Dec 4 2025
Six Sigma Certifications - Reasons Why you Should Get Them
Last updated on Aug 18 2022
5 Lean Continuous Improvement Principles to Supercharge Your Operations
Last updated on Jan 2 2024
Leadership vs Management - The Ultimate Guide
Last updated on May 9 2024
Categories
- Other 83
- Agile Management 49
- Cloud Computing 58
- Project Management 175
- Data Science 71
- Business Management 89
- Digital Marketing 88
- IT Service Management 36
- Programming Language 61
- AI and Machine Learning 94
- IT Security 113
- Quality Management 78
- IT Hardware and Networking 28
- Microsoft Program 5
- Workplace Skill Building 15
- Risk Management 10
- Information Security 8
- Leadership and Management 10
- Corporate Training and Development 1
Trending Now
Top Career benefits of Lean Six Sigma Green Belt
ArticleLean methodology, Six Sigma methodology and Lean Six Sigma Explained
ArticleSix Sigma Black Belt Certification – Value and Career Benefits in 2026
ArticlePareto Chart in Six Sigma - Explained
ArticleSix Sigma Certification Guide - A Professional's Guide
ArticleQuality Control Explained – Six Sigma
ArticleQuality Assurance in Six Sigma Explained
ArticleQuality Assurance vs Quality Control
ArticleTotal Quality Management - A Complete Guide for Beginners
ArticleSix Sigma Certification – Everything you Need to Know About Getting Certified
ArticleLean Six Sigma on Resume for Rewarding Career Benefits
ArticleSix Sigma Yellow Belt Certification - Six Sigma for Beginners
ArticleQuality Management Interview Questions 2026
ArticleQuality Manager Interview Questions and Answers for 2026
ebookService Delivery Manager Interview Questions and Answers (With Examples)
ArticleSix Sigma Interview Questions and Answers 2026
ArticleA Supply Chain Management Guide to Mastering Logistics End to End
ArticleSenior Quality Manager Interview Questions and Answers 2026
ArticleTop Quality Analyst Interview Questions and Answers 2026
ArticleFinancial Analyst Interview Questions and Answers 2026
ArticleRisk Manager Interview Questions and Answers 2026
ArticleCompliance Manager Interview Questions and Answers 2026
ArticleOperation Manager Interview Questions and Answers
ArticleHow to Become a Quality Manager - Career, Job Scope and Certifications
ArticleHow to become a Quality Analyst
ArticleSix Sigma Certifications - Reasons Why you Should Get Them
ArticleTop Qualities of a Good Manager and a Leader
ArticleLearn about Statistical Process Control (SPC) and its top applications
ArticleCost of Poor Quality - A Detailed Guide
ArticleImplementing 5S Methodology for Better Work Efficiency
ArticleWhat Is Lean Management?
ArticleBest Six Sigma Books in 2026
ArticleLeadership vs Management - The Ultimate Guide
ArticleQuality Assurance Plan - Six Steps To Quality Assurance Plan
ArticleOperational Planning Creation, Key Elements and its Benefits
ArticleA Complete Guide to Product Life Cycle Stages 2026
ArticleDMAIC Methodology - The Ultimate Guide
ArticleSix Sigma tools for DMAIC Phases
ArticleWhat Is Lean Manufacturing?- An Overview
ArticleThe Lean Continuous Improvement Model: A Comprehensive Guide
ArticleA Deep Dive into the Power of Lean Continuous Improvement Process
ArticleIntroduction to Lean Manufacturing- Definitions, Framework, and More
ArticleLean Continuous Improvement Methods for Business Excellence
ArticleUnderstanding the Key Principles of Lean Manufacturing
ArticleSecret to Unlock Organizational Excellence: Stages of Continuous Improvement
ArticleLean Continuous Improvement: A Detailed Guide to Mastering Organizational Quality
ArticleLean Waste Management: The Ultimate Guide 2026
ArticleA Deep Dive into Lean Continuous Improvement Tools
Article8 Wastes of Lean - Strategies for Identification and Elimination
Article5 Lean Continuous Improvement Principles to Supercharge Your Operations
ArticleThe Ultimate Guide to Lean Manufacturing
ArticleUnderstanding Lean Manufacturing's Pros and Cons
ArticleLean Waste Reduction Strategies: Boost Efficiency and Cut Costs
ArticleTop 10 Lean Manufacturing Tools for Optimal Productivity
ArticleBeyond the Basics: Benefits of Lean Continuous Improvement
ArticleWhat are Quality Standards? | A Guide to ISO Standards
Article7 Important Types of Quality Management System
ArticleISO 9001 Standard: Benefits and Certification
ArticleA Comprehensive Guide to Quality Management Systems
ArticleBenefits of QMS Certification for Your Business
ArticleStep-by-Step Implementation Guide to ISO 9001
ArticleThe Ultimate Guide to ISO 9001: Boosting Quality and Certification Success
ArticleEssential Components of a Quality Management System
ArticleQuality Management System – QSM Approaches and Methodologies
ArticleHow to Effectively Implement a Robust Quality Management System?
ArticleExplaining QMS Documentation Structure: Benefits and Best Practices
ArticleWho Needs ISO 9001 Certification and Why?
ArticleKey Elements of ISO 9001:2015 Quality Management System
ArticleOvercoming Common Challenges in ISO 9001 Certification: Tips and Best Practices
ArticleBest Quality Management Tools
ArticleTotal Quality Management (TQM) vs. Six Sigma
ArticleQuality Manager Salary: What Freshers & Experts Earn in 2026
ArticleCertified Scrum Product Owner: Job Roles And Responsibilities
ArticleTips for Continuous Integration Testing: Streamlining QA
Article10 Quality Management Strategies Adopted by Top Managers
ArticleDMAIC for Warehouse Safety: From Hazards to Control
ArticleLive Data, Faster Fixes: How Smart Monitoring Is Rewriting Quality Control
Article


















