Random Forest Algorithm: How It Works and Why It Matters
-
 By Sprintzeal
By Sprintzeal - Published on Jan 6 2026
Introduction to Random Forest Algorithm
The random forest algorithm is one of the most powerful and flexible instruments addressed to data scientists in the current world of data science. Understanding its importance requires firstly examining the big picture of machine learning and the role it plays in tech. When defining machine learning, we depict it as a part of AI that concentrates on the creation of such algorithms that can independently learn from data and make predictions without being given explicit instructions.
For those who are new to machine learning, keep your cheat sheet for leverage to quickly identify aspects of algorithms/concepts and keys to that algorithm/concept, and even how to apply it in practice. The Machine Learning Cheat Sheet is designed to provide beginner users an introduction to the importance of cheat sheets for machine learning, reasons why they are helpful to beginner users, and how to use the cheat sheet for various things (interview prep, project work, and personal notes).
The essential machine learning meaning is about the capability of systems to tweak their performance based on accumulated experience. The field in which the random forest algorithm has become extremely popular is characterized by the ability to achieve very high accuracy and work with complicated multidimensional datasets. This random forest algorithm makes use of an ensemble of decision trees. Hence, it avoids the usual errors of single predictive models, like overfitting, i.e., it can extend the model to areas where the data is not used. Going further into the working principles of the random forest algorithm, one gets to know the reason why it is still a predictive analytics tool of the first order and a necessary part of any thorough discussion on the meaning of machine learning and its application developments.
Why Random Forest Is Important in AI & ML
The random forest algorithm is a great example of how a single AI or ML concept can be very instrumental in the progression of the entire field.
Random Forest is the core of the artificial intelligence of the present, thus being a dependable tool in the scenarios of classification and regression that require precision at a high level. Being an ensemble approach, it basically uses the "wisdom of the crowd" principle. That is, several decision trees work together to give a single output that is closer to the truth.
On top of that, the future of machine intelligence is model structures that are able to resist the effect of noise and outliers. Actually, random forest is very good at that. Thus the ai and ml researchers and engineers make the most of it in their work. By doing this, the random forest algorithm prevents any features from dominating the outcome if they are not really useful. It is the stability of the model that is the reason why the algorithm is chosen most of the time when developing situations that can have serious consequences in the field of AI domain.
Random Forest in Modern Machine Learning Applications
Random forest (RF) approach in the work environment is seen in the areas of application driven by the machine learning movement, which is practically limitless. One can name diagnostic health care and fraud detection in the financial sector, to name just a few, where the use of rf has brought fantastic results. By way of example, the random forest algorithm can be the right tool to figure out risk factors for the patients by comparing endless variables at the same time that is insightful for AI phenomena.
In addition to the healthcare field, there are other AI-based sources such as stock market prediction and recommendation engines. Here, the random forest algorithm mainly deals with past data in order to make the most likely future trends and in doing so, it is very consistent. Due to the fact that it is a method capable of working with categorical data as well as numerical data, many machine learning-based applications that are either in the field of computer vision or in the field of natural language processing have been able to use it as a ground for their models. The large-scale implementation of the random forest technique shows that it is a base element in the toolbox of any data scientist who is delving into the frontier of machine learning application potentialities.
What Is Machine Learning?
In order to understand the working of the random forest algorithm, we have to answer the fundamental question of what machine learning is. Basically, it is the way of teaching a mathematical model by means of data in such a way that it becomes capable of making predictions or decisions without any human help. People who want to learn machine learning usually start with the idea of supervised learning, where a model gets the inputs of the data with the labels.
ML is a process to learn from data. The random forest algorithm is one of the best examples of this, as it combines several paths for decision-making in order to come to a final answer. For students and workers who are engaged in learning machine learning, it is very important to be familiar with this particular ensemble method, as it not only solves the problem but also can be easily understood. Knowing machine learning at its fundamental level enables programmers to use the random forest algorithm more effectively in the actual tasks, thus making the ml learning process productive.
Difference Between AI and Machine Learning
People often mix up these terms, but there is a clear distinction between machine learning and artificial intelligence. AI is the big umbrella that includes any system that is aimed at simulating human-like cognitive abilities. To contrast the difference between machine learning and AI first of all, machine learning is a special technique used to train models with data in order to get AI.
By understanding the difference between machine learning and ai, one can better understand the role of the random forest algorithm in the hierarchy. Whereas AI stands for the creation of intelligent agents, machine learning provides the statistical tools, such as the random forest algorithm, to reach that goal. This subtlety is the main difference between machine learning and artificial intelligence: AI is the idea of automated intelligence, and the random forest algorithm is just a practical, algorithmic way that leads to this idea by learning from reality.
Types of Artificial Intelligence
Experts, when referring to different types of artificial intelligence, usually name Narrow AI, General AI, and Superintelligent AI. The random forest algorithm is now considered to be a part of Narrow AI which means that it can perform a few tasks and do them efficiently. Most of the artificial intelligence machine systems that are currently in operation are created for such specialized functions as image recognition or data sorting.
Understanding AI concept types means recognizing different levels of complexity relied on by them. A present-day AI machine could be using the random forest algorithm for structured data processing, while the advanced ones might be led to imitate human logical reasoning eventually. No matter the class, the random forest algorithm is still the number one choice in building an AI machine that is both potent and reliable. The knowledge of the ai concepts is indeed the foundation for acknowledging the random forest algorithm's great value in the tech field.
Exploring the right tools is essential for anyone working in machine learning, as they streamline workflows and enhance model performance. The Machine Learning Tools blog highlights popular platforms, frameworks, and libraries that professionals rely on to build and deploy ML solutions. It’s a practical guide for learners and practitioners to choose the right tools for their projects.
Types of Machine Learning
An understanding of various machine learning types is a must for any professional working with data. In general, the three main categories that describe the way models interact with data form the basis of the machine learning classification. Most machine learning tutorials start with the explanation of the differences between these methods in regard to their training goals and the kind of response they get. Knowing types of machine learning helps us to pinpoint not only the particular model but also, for instance, whether the random forest algorithm is the right choice for the problem at hand.
Supervised Learning
Supervised learning, specifically in the case of the random forest algorithm, is the most directly connected idea of the three main groups. It is a method where the model gets trained on a data set with labels, which means that the output is known in advance. Since the random forest algorithm is used to carry out the prediction of future labels based on the old data. It is, in general, recognized as one of the most dominant supervised machine learning algorithms.
As the mechanism of supervised learning goes, the model is supposed to modify its parameters in such a way as to decrease or eliminate the differences between the prediction results and the real ones. The random forest algorithm accomplishes this task by producing an array of decision trees, each trained on its own subset of data. This strong technique of supervised learning not only confirms that the final model is of high precision but also, most importantly, that it is generalizable. Thus, the target of both classification and regression tasks in the supervised machine learning area, Random Forest is one of the top algorithms.
Unsupervised Learning
It is worthy to note here that the random forest algorithm is generally a supervised learning method and in that sense, it is quite different from unsupervised learning. Here, the program attempts to find the concealed patterns or the natural relations between the entities in the data that are not labeled. Some typical unsupervised learning algorithms are clustering and association, which are used in scenarios where there is no concept of the dependent variable.
Just to mention, the random forest algorithm is a method that achieves its goal by using labels and an unsupervised one is a method that investigates the data in order to find the natural groups. The knowledge of unsupervised learning algorithms is of great importance when one is at the data exploration stage. While the random forest algorithm is about getting to the point in directly answering the questions posed, in unsupervised learning, the questions themselves remain to be discovered, which means that these two are different instruments in data strategy that can be used simultaneously.
Reinforcement Learning
One more interesting area defined by a reinforcement learning tutorial is learning by interaction, the agent-environment loop, where the system learns through trial and error. This approach is a stark contrast to the random forest algorithm that depends on a static dataset.
Random forest algorithm is a predictive one, while reinforcement learning algorithms are prescriptive, i.e., they help in deciding the course of action that should be undertaken at a given moment. To value function estimation, the remote integration of the random forest algorithm in a reinforcement learning framework is something that researchers do occasionally. However, most beginners who go through a reinforcement learning tutorial mainly learn about Markov Decision Processes rather than ensemble trees. Comprehending reinforcement learning algorithms is like looking into the coming times of self-governing systems, which go hand in hand with the consistent capability of the random forest algorithm to predict.
The engineers of machine learning should have various technical abilities, but they should also be trained to use their technical abilities to help them identify and address problems within the machine learning systems they design, develop, deploy, and refine. The blog, Machine Learning Engineer, provides an extensive overview of the job of machine-learning engineering. It describes different responsibilities of a machine-learning engineer, what kind of career paths are available to them, and much more for individuals considering a career in machine learning engineering.
Introduction to Decision Trees
If one wants to grasp the workings of the random forest algorithm, they should first look into what a decision tree is. A decision tree incorporates the elements of the given data on which decisions can be made in a flowchart-like structure. In decision tree machine learning, these models divide the data into branches that eventually lead to a last leaf node indicating a prediction. The decision tree algorithm is known for being easy to understand and its pictorial representation. As it is the core unit that the random forest algorithm is built upon.
How Decision Trees Work
Decision trees are mainly used as a tool for classification machine learning and regression machine learning. The tree, in classification machine learning, categorizes the input data into discrete categories. On the other hand, in regression machine learning, it forecasts uninterrupted numerical values. The decision tree goes through the data by making one choice at a time. Thus, it follows human logic. Nevertheless, a random forest algorithm takes this a step further by combining many trees to come to a collective decision. So, it can be used in both classification machine learning and regression machine learning with enhanced accuracy of predictions.
Limitations of Decision Trees
It is true that decision trees are useful, but a single decision tree also has some drawbacks. The biggest problem is overfitting, whereby the machine learning model becomes so adapted to the training data that it loses the ability to generalize to new data. This limitation makes the model in question very weak when it comes to handling complicated datasets. The random forest algorithm, thus, is a solution to the problem of overfitting, as it combines the results of various trees, thereby producing a more robust machine learning model suitable for real-world application.
What Is the Random Forest Algorithm?
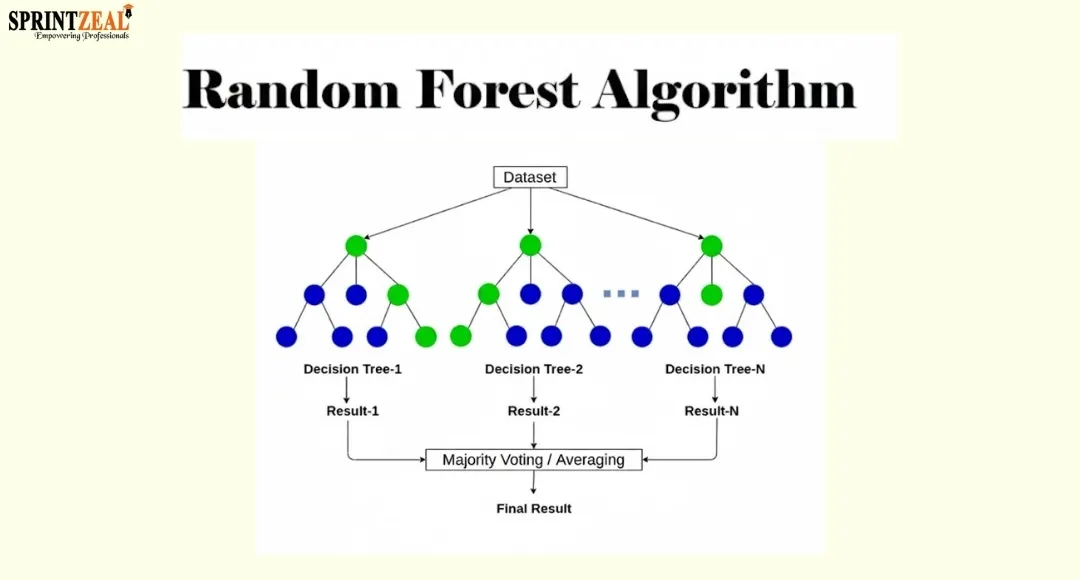
The random forest algorithm in machine learning is, in essence, an ensemble method that achieves its result by creating a large number of decision trees when training. A random forest machine learning scenario implies that each tree being created is slightly different due to random sampling, thus ensuring diversity in the model. The random forest algorithm then returns the class that has been voted most or the average prediction of the individual trees, which makes the random forest algorithm in machine learning a great deal more accurate compared with any one single tree.
How Random Forest Works
The fundamental idea behind the random forest algorithm is ensemble learning, a concept where the result of many weak learners is the strong learner. The forest, through algorithm learning, carries out operations such as bagging and feature randomness to guarantee the uniqueness of each tree. The technique of ensemble learning adopted in this model shields it from overdependence on any single feature. By deploying algorithm learning throughout hundreds of trees, the random forest algorithm is able to attain that level of steadiness, which is very vital in complex data handling.
Random Forest for Classification and Regression
The random forest algorithm is a powerhouse machine learning model that can perform classification tasks for categorical outcomes with high accuracy. Thus, as a random forest in machine learning, it can be used to detect spam or label images, where it will be better than a simple linear model. Besides, it also can act as an effective regressor of continuous data to the same extent. The dual capacity of the random forest algorithm as a machine learning classification tool and a regression tool is pointing to the fact that random forest in machine learning is always the first choice in a production environment.
The key to learning machine learning is learning about the various machine learning algorithm types, examples and their uses. The Machine Learning Algorithms Blog is intended for both newcomers to machine learning as well as those who have experience in this field. This blog has an extensive listing of machine learning algorithm types with examples and provides an overview of the various types of machine learning algorithms and their real-world uses across many industries, giving the user a solid understanding of the basics of machine learning.
Mathematics Behind Random Forest
The random forest algorithm is unlike linear regression machine learning, which fits one line to data, and logistic regression machine learning, which deals with binary outcomes but is weak in handling high-dimensional data. Instead of finding a solution for one equation, the random forest algorithm creates several high-variance trees and then combines them to lower the error. This non-parametric method enables it to model non-linear relationships and be tough in a situation where logistic regression machine learning may be affected by bias, multicollinearity or outliers.
Feature Selection and Feature Importance
One of the essential aspects of feature engineering for machine learning is the identification of influential variables. The random forest algorithm makes the process of feature engineering for machine learning easier by automatically providing Feature Importance scores as a result of impurity reduction. As the model uses random subsets of features for each split, it considers both strong and weak predictors, thus allowing users to concentrate on the most valuable inputs and at the same time reduce the noise.
Training Data and Sampling
The random forest algorithm depends on good training data and employs bootstrapping to generate several subsets of machine learning training data. Different samples are used for each tree, thus lessening the model's sensitivity to data points. By this method, the effect of errors or outliers in the training data is lessened. Thus, the random forest algorithm is more powerful than single models when dealing with imperfect machine learning training data.
Machine Learning Use Cases of Random Forest
The discussion encompassing the healthcare, environmental, and other related fields is not exhaustive but rather indicative of the broad spectrum of different machine learning use cases, where the random forest plays an important role. One of the popular machine learning use case examples in the biomedical domain is the use of random forests to capture subtle patterns of gene expressions for the identification of inherited traits. Another example of unique machine learning use cases within the environmental sciences domain is land-cover mapping and climate forecasting, where the random forest algorithm is used to make ecological predictions based on satellite data with high-level precision.
Random Forest in Data Science & Analytics
What characterizes the professional field of data science and machine learning is unbelievably the same feature that has almost made it a nightmare for other disciplines and that is the ability to extract signal out of noise. An analyst’s arsenal is not complete without the random forest algorithm, which is their go-to instrument for performing exploratory data analysis, since it handles high-dimensional data spaces most effectively. In advance of pure data science, the random forest algorithm is a bridge between data analytics and machine learning that opens the doors for deeper understanding. Whether designing the supply chain processes for optimum results or finding ways of extending product life cycles, the data science machine learning approach coupled with an ensemble method like random forest is a guarantee of rigorous decision-making based on statistics.
Random Forest in Business & Marketing
One of the most tangible examples of the positive impact of machine learning for business can be seen in marketing. Predictions of customer churn and lifetime value based on the random forest algorithm are a common practice in business analytics that lead to retention strategies being most effective. The use of machine learning for business analytics has given the companies the power to target their audience to an extent that was unimaginable before. Marketing teams armed with consumer insights generated by the random forest algorithm can create tailored campaigns that consumers are most likely to respond to. By doing so they make sure that resources are not wasted but rather allocated efficiently. Better ROI is the result of such a strategic use of machine learning for business, as the random forest algorithm is there to reveal the hidden factors that influence the purchasing decisions of the consumers within a machine learning business analytics framework.
Random Forest in Cyber Security
One of the major breakthroughs that have contributed to the rapid advancement of the cybersecurity sector through machine learning is the efficient model like random forest. Due to its outstanding ability to perform anomaly detection, the random forest algorithm plays a vital role in the identification and prevention of network intrusions. When it is allowed to learn from the old traffic samples, the random forest algorithm becomes able to attack the newly occurring events in real-time and thus, in this way, the suspicious activities can be monitored. In machine learning for cybersecurity, being capable of dealing with imbalanced datasets is what makes the model so valuable in this context, because attacks are far fewer than normal traffic. Using the random forest algorithm is a good way for security systems to be adaptive and resilient and, therefore, not be obsolete with the ever-evolving digital threats.
Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence are changing the future of Information Security Management Systems (ISMS) through automation in threat detection, risk assessments, and compliance monitoring. In the blog, AI and Machine Learning in ISMS, it describes how these technologies increase security frameworks and improve resiliency for the organization. This is a highly beneficial read for Cybersecurity professionals who want to integrating Advanced Analytics into their Cybersecurity Strategy.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Random Forest
Understanding the trade-offs is an essential part of properly assessing different machine learning techniques. Among the various models, the random forest algorithm is highly praised for being a robust and powerful predictor. However, it is still not an ideal one. Even though the random forest algorithm lessens the variance problem of single decision trees, it might take a long time for the procedure of training to be done, especially with large datasets. Thus, when deciding on the best option among different machine learning methods, the experts in the field should consider the remarkable precision of the random forest algorithm against the fact that it consumes more memory and takes longer for the predictions than the simpler models.
Benefits Over Other Algorithms
One of the main reasons an AI random forest model is superior to the rest of the top 10 machine learning algorithms is the fact that it is incredibly efficient "out-of-the-box." In contrast to support vector machines or neural networks, the random forest algorithm is very easily adjustable since very few parameters are required. Besides other top 10 machine learning algorithms, it is one of the very few models that provide direct access to the intrinsic features and even double-check the accuracy of the validation step through out-of-bag error estimates. Because of this special character, the random forest algorithm is a very stable benchmark that, most of the time, wins against the rest of the top 10 machine learning algorithms for structured data tasks.
Limitations and Challenges
The random forest algorithm, which has several strengths, is not without its shortcomings and limitations when it comes to the nature of data for machine learning. For example, it might find it difficult to deal with extremely sparse data or a dataset where the number of features is much greater than the number of observations. Besides that, it is very important to collect high-quality data for machine learning since the forest may still be biased if the labels are systematically wrong. Another drawback is its "black box" characteristic. Although it is more understandable than a deep neural network, the random forest algorithm is still less explainable than a single decision tree. Working around these restrictions is an integral part of getting the data ready for machine learning projects that use ensemble methods.
Comparison With Other Machine Learning Algorithms
Among all machine learning algorithms, it is very important to classify tools by their operational logic. Random forest algorithm still holds the first place for structured tabular data even though neural networks are very good at handling unstructured data like video or audio. The random forest algorithm, as an ensemble method, positions itself well between the low complexity of linear models and the high complexity of deep learning when considering all machine learning algorithms as a spectrum. Being familiar with all machine learning algorithms means understanding that the strength of a forest may be more useful than the extreme flexibility of newer architectures in certain cases.
Random Forest vs Decision Tree
The decision tree vs random forest argument usually focuses on the bias-variance trade-off. A single decision tree is easily understandable but it suffers from high variance. The main difference between a decision tree and a random forest is that the random forest algorithm reduces errors by averaging. In a decision tree vs random forest comparison, the individual tree might treat certain data points as noise when in fact they are patterns. However, the random forest algorithm considers this noise as an outlier that disappears when aggregated across many trees. Therefore, the ensemble approach is almost always the winner in the decision tree vs. random forest matchup for any production-level task.
Random Forest vs Linear & Logistic Regression
Besides that, there are considerable architectural differences between the random forest algorithm and the traditional statistical methods when the two are compared. Linear regression in machine learning, for instance, assumes a direct relationship between variables, whereas the random forest algorithm can depict very complicated, non-linear interactions without any prior transformation. By the same token, logistic regression machine learning, being limited by its sigmoid function, cannot do what the random forest algorithm can, i.e., multi-modal distributions among several classes. Even though linear regression in machine learning may be less demanding of computational resources, the random forest algorithm is much more accurate in situations where the data patterns are not obvious or are hidden, thus making it a better alternative to logistic regression machine learning and more versatile.
One of the best ways to get a deep understanding of Machine Learning is through reading good books on the subject. The Best Machine Learning Books blog provides a curated list of books that cover all three levels of learners (beginner, intermediate, and advanced). This guide will help you decide which book may be best suited for your learning style and job/career aspirations.
Learning Path: AI & Machine Learning With Random Forest
If you want to learn ai and machine learning, you have to go through a proper learning path. Most of the time, students start by learning about the structure of data to later understand how individual decision trees work. After exposure to basic concepts, the random forest algorithm in your learning ai and machine learning will signal a new chapter where you will be dealing with ensemble methods instead of simple models. It is said that learning how the random forest algorithm works is the entrance to a more advanced level of machine learning where one learns the key concepts of variance reduction and data sampling, which are foundational to nearly all modern predictive systems.
Machine Learning Courses & Training
Various professionals take machine learning courses to have hands-on exposure. Such a program is intensive in terms of the machine learning training and brings in-depth theoretical and practical issues related to the random forest algorithm. Be it university machine learning courses or online bootcamps, the objective is to supplement the academic knowledge with the practical applications. Top-notch machine learning training will bring in a few projects for you to run the random forest algorithm on the datasets of the real world. Hence, you get acquainted with hyperparameter tuning and model evaluation.
AI & Machine Learning Certification Programs
The ai machine learning certification is a good thing to have if you are a professional who wants to show off your expertise. In fact, receiving a certification in ai and machine learning is a signal for a potential employer that you have a level of skills that is standard and can be trusted in the efficient implementation of models like the random forest algorithm. Usually, the most reliable ai machine learning certification paths have a certain number of lessons dedicated to ensemble learning. When you get certified in ai and machine learning, you become a data-driven leader who is capable of using the random forest algorithm to address complex business challenges and thereby drive company initiatives.
Free vs Paid Machine Learning Courses
Which one to start with: a free machine learning course or a paid course? This is the question that most data scientist aspirants put forward. A free machine learning course is a perfect way to learn the basics of the random forest algorithm without paying a dime. Nonetheless, a free machine learning course can only go so far in terms of "what" and "how," whereas paid programs often offer the guidance and the review by peers that are indispensable for great command of the subject. No matter what you choose, the most important thing is that the curriculum extensively deals with the random forest algorithm, as it is a pillar in the field.
Machine Learning Projects Using Random Forest
The best way to affirm your skills is through real-life application, and starting a machine learning project is a typical portfolio-building requirement. As the random forest algorithm is powerful and effective in dealing with the structured data, it is a number one pick for a first machine learning project. No matter whether you are forecasting the prices of houses or grouping the customer's sentiment, by using the random forest algorithm, you may find out how the ensemble methods raise the results as compared to the individual trees. Apart from that, by finishing a full-fledged machine learning project employing this technique, you get to know the necessity of cross-validation and the measurement of error.
Beginner to Advanced Project Ideas
If you are seeking a beginner machine learning tutorial, then the Titanic Survival Prediction is a typical project idea. In this tutorial that is designed for beginners, you employ the random forest algorithm to estimate the survival results given the passenger information. When you graduate from a machine learning tutorial for beginners, you can challenge yourself with complex projects such as credit scoring or high-frequency trading simulations. These projects on the advanced side of learning require you to perform more intricate random forest algorithm tuning, handle the problem of class imbalances, and deal with time-series data, thus gradually taking you from the fundamental concepts to professional-grade implementations.
Real-World Case Studies
Understanding how a machine learning company implements these instruments gives you a lot of industry insights. For example, a machine learning company in the fintech industry, which is a leader in the sector, may use the random forest algorithm for real-time risk assessment. On the other hand, a machine learning company in the retail industry can utilize the random forest algorithm for the optimization of inventory levels in the warehouses that are located globally. These real-world case studies demonstrate that the random forest algorithm is not a mere concept in theory but a core technology that assists any modern machine learning company to be at the forefront of the competition and data-driven in a rapidly changing market.
Regularization plays an important role in machine learning because of its ability to help reduce the likelihood of models overfitting and thus leading to better model generalization. Throughout the blog, various types of regularization techniques are discussed,, such as L1, L2, and dropout, along with examples demonstrating how these techniques can be applied in real-world scenarios. As such, this blog can provide value to those new to machine learning who want to create more effective and trustworthy machine learning models.
Future of Random Forest and Machine Learning
Random forest algorithm keeps on conforming to new artificial intelligence paradigms as we move further. There will probably be more hybrid models in the future where the forest is used for feature extraction or as a decision layer of deep neural networks. Artificial intelligence engineering is moving its focus to "Green AI," and the random forest algorithm is a good candidate because it is less energy-consuming than huge transformer models.
Trends in AI & ML
The present trends in AI and ML point at a direction of an automated machine learning (AutoML) system where the random forest algorithm is the one selected and tuned by AI software without human intervention. We are here witnessing the birth of an AI machine capable of updating its own internal forests whenever new data arrives. This upgrade of AI software is a guarantee for the continual relevance of the random forest algorithm even at data scales as high as petabytes. Besides that, the deployment of AI machine logic on edge devices is dependent on the forest's simplicity, which allows for local inference.
Role of Random Forest in AI Evolution
The random forest algorithm's heritage is its major stability contribution to machine intelligence. The forest has convinced us that diversity in decision-making is the key to better results and therefore has had a great impact on the way we design most of the current machine intelligence systems. While advancing towards more autonomous and explainable systems, the random forest algorithm is a crucial instrument that provides the performance-transparency equilibrium necessary for the ongoing expansion and ethical utilization of machine intelligence across the globe.
Conclusion
Basically, the random forest algorithm is still one of the key instruments in the toolbox of modern data science. By mitigating the problems that single decision trees have, e.g. high variance and overfitting, this ensemble method offers a trustworthy and accurate structure for pretty much any kind of task. In our journey through ai and machine learning, we have discovered that the random forest algorithm is effective in various sectors, such as healthcare, finance, cybersecurity, and marketing.
The next generation of ai and machine learning, which is predicted to have more complex and autonomous systems, will still rely on the concepts of the random forest algorithm to lead the way. The reason why it is a favorite tool among both novices and professionals is that it can easily identify the most important features, work with vast datasets, and its performance can be hardly degraded by a lack of tuning. If you are a beginner in the field of ai and machine learning or you are an experienced professional, learning the random forest algorithm is the minimum requirement to create models that can effectively handle the data-rich world of the future.
If you are a professional aiming to excel in the random forest algorithm and learn other advanced technologies in machine intelligence, the Sprintzeal AI and Machine Learning Master Program is the right choice with its complete and industry-aligned curriculum.
Do you want to move forward with your career as an AI engineer? Please contact our worldwide assistance team to know about the enrollment, get a personalized corporate training plan, or if you have any other queries related to the course.
FAQs for Random Forest Algorithm
What is Random Forest?
A Random Forest is an ensemble method for learning, and it makes use of a number of decision trees.
Why is it called “Random”?
It employs random subsets of both the data and the features to build diverse trees, thereby fighting against the problem of overfitting.
Which problems can a Random Forest solve?
Applying to both classification and regression tasks, this is quite effective.
How does it improve accuracy?
Because the predictions are averaged over several trees, it lowers variance.
Are there issues of overfitting in the Random Forest algorithm?
Compared to single decision trees, but can overfit if there are too many decision trees or features.
What are the primary benefits?
High accuracy, robust to noise, and it can process large databases with a high number of features.
What are the limitations?
It can be computationally costly and difficult to interpret relative to simpler models.
How many trees are to be used?
More trees imply an improvement in performance, but eventually, the improvement becomes negligible.
Does Random Forest allow missing values?
Yes, it can handle missing values quite well with surrogate splits.
Can Random Forest perform feature selection?
Yes, it does offer a measure of importance, which can be used to identify important predictors.
Subscribe to our Newsletters
Popular Programs
Trending Posts
Machine Learning Regression Analysis Explained
Last updated on May 18 2023
Top 10 Career Opportunities in Artificial Intelligence
Last updated on Oct 5 2023
Gemini Vs ChatGPT: Comparing Two Giants in AI
Last updated on Aug 20 2025
Top AI Certifications: A Guide to AI and Machine Learning in 2026
Last updated on Dec 20 2024
Types Of Artificial Intelligence and its Branches
Last updated on Jan 30 2023
What Are Small Language Models?
Last updated on Dec 30 2025
Categories
- Other 71
- Agile Management 48
- Cloud Computing 57
- Project Management 174
- Big Data 67
- Business Management 88
- Digital Marketing 81
- IT Service Management 29
- Programming Language 59
- AI and Machine Learning 85
- IT Security 112
- Quality Management 78
- IT Hardware and Networking 26
- Microsoft Program 5
- Workplace Skill Building 14
- Risk Management 9
- Information Security 8
- Leadership and Management 9
- Corporate Training and Development 1
Trending Now
Consumer Buying Behavior Made Easy in 2026 with AI
Article7 Amazing Facts About Artificial Intelligence
ebookMachine Learning Interview Questions and Answers 2026
ArticleHow to Become a Machine Learning Engineer
ArticleData Mining Vs. Machine Learning – Understanding Key Differences
ArticleMachine Learning Algorithms - Know the Essentials
ArticleMachine Learning Regularization - An Overview
ArticleMachine Learning Regression Analysis Explained
ArticleClassification in Machine Learning Explained
ArticleDeep Learning Applications and Neural Networks
ArticleDeep Learning vs Machine Learning - Differences Explained
ArticleDeep Learning Interview Questions - Best of 2026
ArticleFuture of Artificial Intelligence in Various Industries
ArticleMachine Learning Cheat Sheet: A Brief Beginner’s Guide
ArticleArtificial Intelligence Career Guide: Become an AI Expert
ArticleAI Engineer Salary in 2026 - US, Canada, India, and more
ArticleTop Machine Learning Frameworks to Use
ArticleData Science vs Artificial Intelligence - Top Differences
ArticleData Science vs Machine Learning - Differences Explained
ArticleCognitive AI: The Ultimate Guide
ArticleTypes Of Artificial Intelligence and its Branches
ArticleWhat are the Prerequisites for Machine Learning?
ArticleWhat is Hyperautomation? Why is it important?
ArticleAI and Future Opportunities - AI's Capacity and Potential
ArticleWhat is a Metaverse? An In-Depth Guide to the VR Universe
ArticleTop 10 Career Opportunities in Artificial Intelligence
ArticleExplore Top 8 AI Engineer Career Opportunities
ArticleA Guide to Understanding ISO/IEC 42001 Standard
ArticleNavigating Ethical AI: The Role of ISO/IEC 42001
ArticleHow AI and Machine Learning Enhance Information Security Management
ArticleGuide to Implementing AI Solutions in Compliance with ISO/IEC 42001
ArticleThe Benefits of Machine Learning in Data Protection with ISO/IEC 42001
ArticleChallenges and solutions of Integrating AI with ISO/IEC 42001
ArticleFuture of AI with ISO 42001: Trends and Insights
ArticleTop 15 Best Machine Learning Books for 2026
ArticleTop AI Certifications: A Guide to AI and Machine Learning in 2026
ArticleHow to Build Your Own AI Chatbots in 2026?
ArticleGemini Vs ChatGPT: Comparing Two Giants in AI
ArticleThe Rise of AI-Driven Video Editing: How Automation is Changing the Creative Process
ArticleHow to Use ChatGPT to Improve Productivity?
ArticleTop Artificial Intelligence Tools to Use in 2026
ArticleHow Good Are Text Humanizers? Let's Test with An Example
ArticleBest Tools to Convert Images into Videos
ArticleFuture of Quality Management: Role of Generative AI in Six Sigma and Beyond
ArticleIntegrating AI to Personalize the E-Commerce Customer Journey
ArticleHow Text-to-Speech Is Transforming the Educational Landscape
ArticleAI in Performance Management: The Future of HR Tech
ArticleAre AI-Generated Blog Posts the Future or a Risk to Authenticity?
ArticleExplore Short AI: A Game-Changer for Video Creators - Review
Article11 Undetectable AI Writers to Make Your Content Human-Like in 2026
ArticleHow AI Content Detection Will Change Education in the Digital Age
ArticleWhat’s the Best AI Detector to Stay Out of Academic Trouble?
ArticleAudioenhancer.ai: Perfect for Podcasters, YouTubers, and Influencers
ArticleHow AI is quietly changing how business owners build websites
ArticleMusicCreator AI Review: The Future of Music Generation
ArticleHumanizer Pro: Instantly Humanize AI Generated Content & Pass Any AI Detector
ArticleBringing Your Scripts to Life with CapCut’s Text-to-Speech AI Tool
ArticleHow to build an AI Sales Agent in 2026: Architecture, Strategies & Best practices
ArticleRedefining Workforce Support: How AI Assistants Transform HR Operations
ArticleTop Artificial Intelligence Interview Questions for 2026
ArticleHow AI Is Transforming the Way Businesses Build and Nurture Customer Relationships
ArticleBest Prompt Engineering Tools to Master AI Interaction and Content Generation
Article7 Reasons Why AI Content Detection is Essential for Education
ArticleTop Machine Learning Tools You Should Know in 2026
ArticleMachine Learning Project Ideas to Enhance Your AI Skills
ArticleWhat Is AI? Understanding Artificial Intelligence and How It Works
ArticleHow Agentic AI is Redefining Automation
ArticleThe Importance of Ethical Use of AI Tools in Education
ArticleFree Nano Banana Pro on ImagineArt: A Guide
ArticleDiscover the Best AI Agents Transforming Businesses in 2026
ArticleEssential Tools in Data Science for 2026
ArticleLearn How AI Automation Is Evolving in 2026
ArticleGenerative AI vs Predictive AI: Key Differences
ArticleHow AI is Revolutionizing Data Analytics
ArticleWhat is Jasper AI? Uses, Features & Advantages
ArticleWhat Are Small Language Models?
ArticleWhat Are Custom AI Agents and Where Are They Best Used
ArticleAI’s Hidden Decay: How to Measure and Mitigate Algorithmic Change
ArticleAmbient Intelligence: Transforming Smart Environments with AI
ArticleConvolutional Neural Networks Explained: How CNNs Work in Deep Learning
ArticleAI Headshot Generator for Personal Branding: How to Pick One That Looks Real
ArticleWhat Is NeRF (Neural Radiance Field)?
ArticleWhat is Causal Machine Learning and Why Does It Matter?
ArticleThe Professional Guide to Localizing YouTube Content with AI Dubbing
Article










