Convolutional Neural Networks Explained: How CNNs Work in Deep Learning
-
 By Arya Karn
By Arya Karn - Published on Jan 13 2026
Have you ever looked at something and instantly recognised it without thinking? Convolutional Neural Networks mimic that biological process. They get ideas from how the human visual brain analyses information in steps, starting with simple shapes and moving on to more complicated ones. As you’ll see in this cnn explained guide, CNNs have become essential in modern AI because they combine accuracy, speed, and the ability to handle massive image datasets with minimal preprocessing.
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs)
- How a Convolutional Neural Network Works
- Key Components of a CNN Architecture
- Types of Convolutional Neural Networks
- Applications of CNNs in the Real World
- Advantages & Limitations of Convolutional Neural Networks
- CNN vs Other Neural Networks
- Training a Convolutional Neural Network
- Future of CNNs in AI
- Conclusion
- FAQ’s on Convolutional Neural Networks
Introduction to Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs)
A Convolutional Neural Network is a special kind of deep learning model that aims to mimic human visual perception to some extent. Whenever you think about how machines are able to comprehend faces, find objects, or categorize images, CNNs are the answer. CNN accomplishes this feat by convolutional operations—filters that are mathematical in nature and that go over an image and pick out the most relevant features, such as edges, curves, shapes, and textures.
In deep learning, the purpose of a CNN is simple yet powerful: to automatically learn features from data without manual feature engineering. This makes them highly efficient for image-based tasks and a major breakthrough in computer vision.
How a Convolutional Neural Network Works
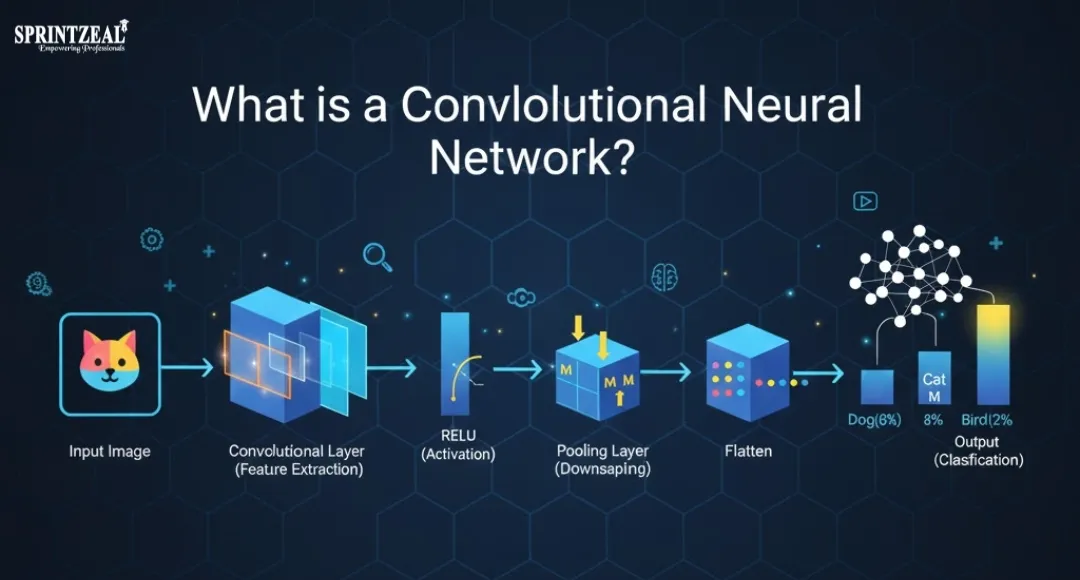
The picture above is a great illustration of how a Convolutional Neural Network takes an input and goes through it step by step. The architecture is explained in a very clear, point-wise way:
Convolutional Layer – Feature Extraction
- Runs convolutional filters over the image.
- Identifies edges, textures, and even the pattern of a zebra stripe in the example.
ReLU Activation – Gives Non-Linearity
- Removes negative values.
- Helps the model learn complex and non-linear visual patterns.
Pooling Layer – Reduces Dimensions
- Compresses feature maps by selecting the most important information.
- As shown in the image, the maps become smaller but richer in meaning.
Fully Connected Layer – Makes Decisions
- Combines all extracted features.
- Learns which patterns belong to each class.
Softmax Layer – Converts Outputs to Probabilities
- Produces probability scores (e.g., Zebra = 0.7 in the image).
- Allows the network to choose the most likely class.
In a Convolutional Neural Network, convolutional operations are the core mechanism that helps the model understand visual data. A filter (or kernel) slides across the image and multiplies small pixel regions to detect patterns like edges, curves, or textures. Think of it as a digital magnifying glass focusing on tiny details. Different filters extract different features, which is why CNNs recognize complex images so accurately.
Did you know a single image can generate dozens of filters, each capturing a unique pattern?
When a filter scans an image, the result is a feature map—a new 2D representation showing where specific features exist. In this cnn explained process, shallow layers detect simple shapes while deeper layers capture meaningful structures like eyes, stripes, or objects. Feature maps help the network understand “what” and “where” certain patterns appear
Once feature maps are generated, the Convolutional Neural Network must learn which patterns are correct. This happens through backpropagation, where the model compares its prediction with the actual label and calculates error. The network then adjusts weights inside each convolutional filter to improve accuracy. Over many iterations, CNNs refine their ability to detect patterns and reduce mistakes.Backpropagation is like feedback—each correction makes the model smarter. This is how CNNs learn to identify objects with near-human precision
Key Components of a CNN Architecture
A Convolutional Neural Network is built using several core components that work together to extract features, reduce noise, and make accurate predictions. Understanding these components is crucial to fully grasp how the convolutional process works in deep learning.
Stride, Padding, and Filter Size Explained with Examples
In any cnn explained workflow, three elements shape the output of a convolution:
- Filter Size: Determines how much of the image a kernel looks at.
For example, a 3×3 filter captures very fine details, while a 7×7 filter captures broader patterns. - Stride: Controls how far the filter moves each step.
A stride of 1 produces detailed feature maps; stride 2 makes them smaller and faster to compute. - Padding: Adds extra pixels around the image.
Same padding keeps output size equal; valid padding reduces it.
Pooling Types: Max Pooling vs Average Pooling
Pooling reduces spatial size while keeping essential information.
- Max Pooling takes the highest value in each region—great for highlighting strong features.
- Average Pooling averages values—useful when smoothness is needed.
This step helps a Convolutional Neural Network become faster and more robust to noise.
Activation Functions Used in CNNs
Activation functions add non-linearity:
- ReLU: Fast and widely used; keeps positive values.
- Sigmoid: Good for binary outputs.
- TanH: Centers data between –1 and 1 for stable learning.
Dropout and Regularization Techniques in CNNs
To prevent overfitting, CNNs use:
- Dropout: Randomly turns off neurons during training.
- L2 Regularization: Reduces overly large weights.
- Batch Normalization: Stabilizes and speeds up learning.
Types of Convolutional Neural Networks
Depending on the architecture, depth, and kind of the input data, a Convolutional Neural Network may be any of several different forms. CNNs have, in fact, gradually changed from straightforward models to deeply refined, scalable, and lightweight designs the core of which is today's AI systems. In this cnn illustrated part, let's firstly define what types of CNNs are and how each of them transformed deep learning.
Classic CNN Models
Classic structures were the ones that bravely paved the road of modern vision-based computer methods.
- LeNet-5 (1998): Among the very first convolutional models, it was made for digits recognition tasks such as MNIST.
- AlexNet (2012): A landmark network that lowered ImageNet errors by making use of more layers, ReLU activation, and GPU-based training.
- VGGNet (2014): It gained its fame by a very simple and neat idea of consecutive 3×3 convolutional layers, thus a minimalist architecture achieving high accuracy.
These algorithms were the main proofs of the idea that going deeper with neural networks leads to better results.
Modern CNN Architectures
Contemporary projects had goals to use resources more efficiently, to remove obstacles during the models' training, and to optimize the machine's calculations:
- ResNet: The new features that it presented were the skip connections which in return made it possible for the networks that have a very high number of layers (50–152) to be trained without the problem of vanishing gradients.
- Inception: The scheme of parallel multi-scale convolutions (1×1, 3×3, 5×5) allows the network to get diverse features all at one go.
- MobileNet: Made use of depthwise separable convolutions to serve mobile and edge devices in a way that it is quite small and runs fast.
Those are the nets that keep running the real-time tasks like face recognition, autonomous driving, and mobile AI.
1D, 2D, and 3D CNNs
Convolutional neural networks differ by the dimensions they take as input:
- 1D CNNs: Are those that work on sequential data such as text, audio, and time-series signals.
- 2D CNNs: The mostly referred to are those that do the processing on height × width grids, the best examples being images.
- 3D CNNs: The reasoning behind this extension is that the filter should not only capture the length and breadth but also the depth of the movement or volume data thus it is utilized in video analysis and medical scans (MRI, CT).
If you want to know more about deep learning hwo it is connected to neural networks. Check out this blog on Deep Learning and Neural Networks
Applications of CNNs in the Real World
Convolutional Neural Network is the main engine behind many of the AI systems that we use daily and it is, therefore, one of the most powerful deep learning tools in modern AI. Simply said, CNNs are now everywhere where machine learning tools is used to "see" something, whether it is a natural image or a medical scan, and the network figures out the patterns by itself using convolutional operations—a thing that traditional methods could hardly do.
In computer vision, CNNs are used for object classification, movement tracking, and image segmentation, thus enabling advanced analytics. The medical field is incredibly well served as CNNs can read MRI, X-ray, and CT images with high precision and in a very short time, thus very often, they are the first to detect that a certain condition has been established.
In the field of Natural Language Processing, one-dimensional convolutional neural networks are used for the analysis of text sequences to provide understanding of context, intent, and sentiment. In addition, in autonomous platforms like self-driving cars and smart robots, CNNs help them to understand their surroundings in real-time to achieve safety and accuracy.
CNNs in Computer Vision
Computer vision is one of the most popular applications in any cnn explained guide. CNNs are good at this because they can directly grasp the visual patterns by their convolutional layers.
- Image Classification: Figures out what object is shown in the image (cat, car, dog, etc.).
- Object Detection: Finds and tags the objects in a picture, for instance, detecting pedestrians or vehicles.
- Image Segmentation: Breaks images into pixel-level regions, useful in medical, navigation, and editing tools.
Ever wondered how your phone recognizes your photos instantly? A Convolutional Neural Network is working behind the scenes.
CNNs in Medical Imaging
CNNs are transforming healthcare by analyzing complex medical images:
- MRI, X-ray and CT Scan Interpretation: Extracts structural patterns to detect abnormalities.
- Disease Detection: Identifies tumors, fractures, pneumonia, and more.
- Faster Diagnostics: Helps doctors make quicker and more accurate decisions.
With convolutional feature extraction, a Convolutional Neural Network can spot tiny details often missed by the human eye.
CNNs in NLP Using 1D CNNs
1D CNNs process text sequences just like they process signals. They help with:
- Text Classification
- Sentence Modeling
- Intent and Sentiment Analysis
In many cnn explained workflows, 1D CNNs outperform RNNs for short, fixed-length text tasks because they learn local patterns efficiently.
CNNs in Autonomous Vehicles, Robotics, and Face Recognition
A Convolutional Neural Network is essential for machines that need to “see” and react in real time.
- Path Detection: Assists self-driving cars in lane keeping that is precise.
- Obstacle Detection: Locates pedestrians, traffic signs, and other vehicles.
- Robotics: Gives the capability to robots to pick up items, move in areas, and recognize surroundings.
- Face Recognition & Biometrics: CNNs examine facial landmarks and identity confirmation is done to the person with whom the highest accuracy.
Quick thought: Just think of a robot without CNNs—how would it figure out what to take or stay away from?
Advantages & Limitations of Convolutional Neural Networks
A Convolutional Neural Network offers powerful capabilities for understanding visual and sequential data, and any “cnn explained” guide highlights why they dominate modern AI systems. Their convolutional layers learn patterns automatically, reducing the need for manual feature engineering. But while CNNs deliver high accuracy and automation, they also come with notable limitations like computational cost and data dependency.
Benefits of CNNs
CNNs are the best mainly because they are capable of feature extraction on their own from convolutional filters therefore there is no need for manual-feature engineering. Consequently, in general, accuracies become higher especially in such areas as computer vision, medical imaging and face recognition. Their convolutional architecture enables them to find very simple (edges) in the first layers and very complicated (objects) in the deeper layers, thus, they become very strong and can be used for a large number of problems. A Convolutional Neural Network is also capable of reducing the intervention of humans which is helpful in the process of automating tasks like classification, detection, and segmentation.
If someone is looking for a simple explanation of "cnn explained" then he should consider a model which learns patterns just like humans do by seeing multiple examples.
Challenges of CNNs
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) need a lot of data to be able to generalize well; otherwise, they tend to overfit or yield low performance in real-world tasks. Moreover, they are quite costly in terms of computation, particularly when deeper architectures are involved. Usually, a GPU is required for the training of a CNN due to the fact that convolutional operations are very intensive in terms of processing power. A further issue is interpretability, i.e., CNNs are considered as black boxes, thus it is rather difficult to comprehend their decisions.. So even though “cnn explained” articles may simplify them, real-world deployment requires careful tuning, regularization, and resource planning.
CNN vs Other Neural Networks
A Convolutional Neural Network works differently from other neural networks because it processes data using convolutional filters that automatically learn spatial patterns. In this cnn explained comparison, CNNs excel in image, video, and spatial tasks, while ANNs and RNNs shine in other domains. ANNs rely on dense, fully connected layers and are used for tabular, numerical, and basic classification tasks. RNNs specialize in sequential information such as speech, text, and time series by retaining memory of previous inputs.
Here’s something interesting to think about—why do CNNs recognize shapes so accurately while RNNs master sentence flow?
Vision Transformers introduce a modern alternative with their global attention mechanism, performing exceptionally well on large datasets. Each architecture serves a distinct purpose depending on the data structure and task requirements.
-
CNN vs ANN: Key Differences
ANNs rely solely on dense layers, with each neuron being connected to every other neuron. This makes them suitable for tasks such as tabular data, numerical prediction, and classification of a simple nature. A Convolutional Neural Network, however, employs convolutional layers that move filters over images in order to detect spatial patterns such as edges, corners, and textures. In this way, CNNs can preserve spatial structure and have fewer parameters than ANNs, thus logrithmically they outperform ANNs on visual data. The architecture of networks is geared towards pattern recognition within grid-like inputs, which is why they are the most used in computer vision.
-
CNN vs RNN: What & When to Use?
RNNs are capable of handling sequence-based data such as text, audio, and chronological signals because they can maintain context through recurrent connections. In contrast, a Convolutional Neural Network is the best solution for spatial data like images, videos, and sensor heatmaps due to its convolutional feature extraction. Each of the two architectures has different advantages, and the hybrid CNN–RNN models are usually employed in video captioning and multimodal learning. In other words, RNNs are the right choice when the order and temporal flow are important, whereas CNNs are the best when the spatial structure and pattern recognition are necessary.
-
CNN vs Vision Transformers (ViTs)
Vision Transformers use an attention mechanism which considers all image patches at once, instead of processing them with sliding convolutional filters one by one. By having less inductive bias than a conventional Convolutional Neural Network, ViTs don't have the assumption of how features should be arranged - they learn everything straight from the data. Such a capability makes ViTs very potent on large datasets, where sufficient samples allow models to learn global relationships effectively. However, CNNs are still able to perform well on smaller datasets because of their inherent spatial priors and feature extraction that is efficient. So, CNNs and ViTs are two powerful but different choices in modern computer vision.
Training a Convolutional Neural Network
Training a Convolutional Neural Network is a step-by-step, engineering-focused operation that goes from strong data preparation to very detailed model evaluation. In this cnn explained guide, the work flow turns the focus on preparing top-notch image datasets-resizing, normalising, and augmenting them to assure uniform training.
After the data pipeline is sorted out, you design the model with convolutional layers for feature extraction, pooling layers for dimensionality reduction, and dense layers for the final decision-making.
Do you know why a CNN works better when images are normalised? Because Normalization keeps pixel values within a similar distribution, which makes the model converge faster and helps in reducing gradient instability.
After that, training is done through iterative backpropagation, whereby the model adjusts weights using a suitable optimiser. To end with, evaluation metrics like accuracy, F1-score, and confusion matrices show the model’s performance in the real world and its ability to generalise.
Steps to Build and Train a CNN Model
- Different specialists normally develop a Convolutional Neural Network following these subsequent processes:
- Load the Dataset – Pull in structured visual datasets such as CIFAR-10, ImageNet, or customize pipelines.
- Preprocess Images – Change the size, normalize, and extend the data so that the model will generalize better.
- Design the Architecture – Insert layers for convolution, pooling, dropout, and fully-connected layers.
- Compile the Model – Set up loss functions, optimizers (Adam/SGD), and evaluation metrics.
- Train the Network – Go through multiple epochs and batches.
- Evaluate – Use the metrics for the images that the model has never seen before to find the areas where the performance is lacking.
This comprehensive CNN pipeline is the main structure of those computer vision systems which are at a production level.
Hyperparameters to Tune in CNNs
If the hyperparameters are changed, it can highly change the efficiency of a Convolutional Neural Network to learn:
- Learning Rate:
This parameter regulates the changes of weights very substantially.
- Batch Size:
This specification is responsible for the amount of memory that is needed and also the stability of training.
- Filter Size:
This element determines the level of detail of the image that the convolutional layer will use to extract features.
- Epochs:
It tells for how long the training process will be.
- Optimizer:
Adam, SGD, and RMSProp are the three optimizers that behave differently while converging.
Using Frameworks Like TensorFlow and PyTorch
With modern frameworks one can easily build and deploy Convolutional Neural Network architectures that are:
- TensorFlow:
It is really good for sending models to production, serving, and distributed training.
- PyTorch:
It is preferred in research because of its dynamic graphs and very user-friendly API.
- GPU/TPU Acceleration:
It is what makes training fast and allows for quick experiments with complex convolutional models.
- Rich Tooling:
With the help of the development tools like TensorBoard, TorchMetrics and integrated debuggers the development cycle is getting smoother.
Both platforms make it easy for professionals to prototype, optimize, and scale CNN models in real-world AI workflows.
Future of CNNs in AI
The future of the Convolutional Neural Network is evolving rapidly as AI systems demand more efficiency, accuracy, and real-time adaptability. In this cnn explained overview, CNNs are moving beyond traditional image tasks and becoming integral to generative AI, diffusion-powered creativity, and on-device intelligence. Their convolutional structure is being optimized for lightweight, energy-efficient execution without compromising performance.
Why are lightweight CNNs becoming more important today? Because modern applications require fast, on-device inference on mobiles, wearables, and IoT devices without reliance on cloud GPUs.
CNNs are also being redesigned for emerging AI workloads such as multimodal learning, 3D perception, and autonomous systems. The future points toward hybrid architectures where CNNs collaborate with Transformers and diffusion models for better scalability and realism.
Role of CNNs in Generative AI and Diffusion Models
In generative AI, a Convolutional Neural Network plays a crucial supporting role by acting as a powerful feature extractor. CNNs enhance diffusion models by improving how visual features—textures, boundaries, gradients—are interpreted and reconstructed during image generation. Their convolutional layers help diffusion architectures maintain structural consistency, ensuring outputs look sharper and more realistic. This cnn explained integration strengthens image synthesis pipelines, making modern generative models more detailed and controllable.
Edge Deployment of CNNs with TinyML
Edge AI relies heavily on optimized Convolutional Neural Network designs that fit within the constraints of low-power hardware. TinyML enables deploying convolutional models on microcontrollers, mobile devices, cameras, and IoT sensors. Techniques like quantization, pruning, and model distillation reduce model size while preserving accuracy.
This shift empowers real-time vision tasks such as face unlock, gesture control, and anomaly detection directly on devices.
Upcoming Trends and Research in CNN Optimization
Future studies in the area of Convolutional Neural Network optimization revolve around making models that are quicker, smaller, and more capable of adapting. Some of the main trends are efficient CNN architectures such as MobileNetV3 and EfficientNet that deliver great performance with a minimal amount of computation. Pruning techniques are intended to eliminate redundant neurons and filters, thereby improving the speed of convolutional layers. Neural Architecture Search (NAS) is a method that changes the structure of CNN topologies by finding the most suitable ones for a particular hardware automatically. On the other hand, hardware improvements – AI accelerators, edge TPUs, and FPGA-friendly designs – are there to make sure that CNNs can keep growing in their real-world applications. This trend points to a large-scale change of the kind of AI systems that are still powerful but more sustainable
Conclusion
Convolutional Neural Networks are still the main reason behind the big changes that AI is getting in the areas of vision, healthcare, robotics, and generative models, them becoming faster and more efficient architectures for the new applications. AI isn't science fiction anymore; it’s your co-worker. The question is, are you going to master it, or let it master you? Get ahead of the biggest tech wave in history. Learn how to build and deploy intelligent systems with Sprintzeal’s Artificial Intelligence Certification Training.
FAQ’s on Convolutional Neural Networks
1. Are CNNs still used in 2026?
Yes — CNNs are definitely still in use in 2026. In spite of next-gen models like Vision Transformers and big foundation models gaining popularity, Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) are still viable in numerous practical scenarios, particularly, situations that require high efficiency, low data consumption, and fast processing.
2. Where is CNN mostly used ?
CNNs are mostly used in image-focused tasks such as object detection, facial recognition, medical imaging, and video analysis, where extracting spatial patterns through convolutional operations is essential.
3. Is CNN part of deep learning?
Absolutely, a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) is fundamentally a deep learning architecture that is mainly developed for handling visual and spatial data. It is basically the go-to deep learning model for tasks involving images, videos, and pattern recognition.
4. What are the 4 layers of CNN?
There are four layers in CNN :
- Convolution Layer,
- Activation Function Layer
- Pooling Layer
- Full Connectedness (Fully Connected Layer)
5. What are the real life applications of convolution?
It has applications that include probability, statistics, computer vision, image and signal processing, electrical engineering, and differential equations.
Subscribe to our Newsletters
Popular Programs
Trending Posts
Top Machine Learning Frameworks to Use
Last updated on Feb 28 2024
AI and Future Opportunities - AI's Capacity and Potential
Last updated on Jun 8 2023
Data Mining Vs. Machine Learning – Understanding Key Differences
Last updated on Dec 22 2023
Top Artificial Intelligence Interview Questions for 2026
Last updated on Oct 15 2025
Top Machine Learning Tools You Should Know in 2026
Last updated on Oct 22 2025
Random Forest Algorithm: How It Works and Why It Matters
Last updated on Jan 6 2026
Categories
- Other 71
- Agile Management 48
- Cloud Computing 57
- Project Management 174
- Big Data 67
- Business Management 88
- Digital Marketing 81
- IT Service Management 29
- Programming Language 59
- AI and Machine Learning 85
- IT Security 112
- Quality Management 78
- IT Hardware and Networking 26
- Microsoft Program 5
- Workplace Skill Building 14
- Risk Management 9
- Information Security 8
- Leadership and Management 9
- Corporate Training and Development 1
Trending Now
Consumer Buying Behavior Made Easy in 2026 with AI
Article7 Amazing Facts About Artificial Intelligence
ebookMachine Learning Interview Questions and Answers 2026
ArticleHow to Become a Machine Learning Engineer
ArticleData Mining Vs. Machine Learning – Understanding Key Differences
ArticleMachine Learning Algorithms - Know the Essentials
ArticleMachine Learning Regularization - An Overview
ArticleMachine Learning Regression Analysis Explained
ArticleClassification in Machine Learning Explained
ArticleDeep Learning Applications and Neural Networks
ArticleDeep Learning vs Machine Learning - Differences Explained
ArticleDeep Learning Interview Questions - Best of 2026
ArticleFuture of Artificial Intelligence in Various Industries
ArticleMachine Learning Cheat Sheet: A Brief Beginner’s Guide
ArticleArtificial Intelligence Career Guide: Become an AI Expert
ArticleAI Engineer Salary in 2026 - US, Canada, India, and more
ArticleTop Machine Learning Frameworks to Use
ArticleData Science vs Artificial Intelligence - Top Differences
ArticleData Science vs Machine Learning - Differences Explained
ArticleCognitive AI: The Ultimate Guide
ArticleTypes Of Artificial Intelligence and its Branches
ArticleWhat are the Prerequisites for Machine Learning?
ArticleWhat is Hyperautomation? Why is it important?
ArticleAI and Future Opportunities - AI's Capacity and Potential
ArticleWhat is a Metaverse? An In-Depth Guide to the VR Universe
ArticleTop 10 Career Opportunities in Artificial Intelligence
ArticleExplore Top 8 AI Engineer Career Opportunities
ArticleA Guide to Understanding ISO/IEC 42001 Standard
ArticleNavigating Ethical AI: The Role of ISO/IEC 42001
ArticleHow AI and Machine Learning Enhance Information Security Management
ArticleGuide to Implementing AI Solutions in Compliance with ISO/IEC 42001
ArticleThe Benefits of Machine Learning in Data Protection with ISO/IEC 42001
ArticleChallenges and solutions of Integrating AI with ISO/IEC 42001
ArticleFuture of AI with ISO 42001: Trends and Insights
ArticleTop 15 Best Machine Learning Books for 2026
ArticleTop AI Certifications: A Guide to AI and Machine Learning in 2026
ArticleHow to Build Your Own AI Chatbots in 2026?
ArticleGemini Vs ChatGPT: Comparing Two Giants in AI
ArticleThe Rise of AI-Driven Video Editing: How Automation is Changing the Creative Process
ArticleHow to Use ChatGPT to Improve Productivity?
ArticleTop Artificial Intelligence Tools to Use in 2026
ArticleHow Good Are Text Humanizers? Let's Test with An Example
ArticleBest Tools to Convert Images into Videos
ArticleFuture of Quality Management: Role of Generative AI in Six Sigma and Beyond
ArticleIntegrating AI to Personalize the E-Commerce Customer Journey
ArticleHow Text-to-Speech Is Transforming the Educational Landscape
ArticleAI in Performance Management: The Future of HR Tech
ArticleAre AI-Generated Blog Posts the Future or a Risk to Authenticity?
ArticleExplore Short AI: A Game-Changer for Video Creators - Review
Article11 Undetectable AI Writers to Make Your Content Human-Like in 2026
ArticleHow AI Content Detection Will Change Education in the Digital Age
ArticleWhat’s the Best AI Detector to Stay Out of Academic Trouble?
ArticleAudioenhancer.ai: Perfect for Podcasters, YouTubers, and Influencers
ArticleHow AI is quietly changing how business owners build websites
ArticleMusicCreator AI Review: The Future of Music Generation
ArticleHumanizer Pro: Instantly Humanize AI Generated Content & Pass Any AI Detector
ArticleBringing Your Scripts to Life with CapCut’s Text-to-Speech AI Tool
ArticleHow to build an AI Sales Agent in 2026: Architecture, Strategies & Best practices
ArticleRedefining Workforce Support: How AI Assistants Transform HR Operations
ArticleTop Artificial Intelligence Interview Questions for 2026
ArticleHow AI Is Transforming the Way Businesses Build and Nurture Customer Relationships
ArticleBest Prompt Engineering Tools to Master AI Interaction and Content Generation
Article7 Reasons Why AI Content Detection is Essential for Education
ArticleTop Machine Learning Tools You Should Know in 2026
ArticleMachine Learning Project Ideas to Enhance Your AI Skills
ArticleWhat Is AI? Understanding Artificial Intelligence and How It Works
ArticleHow Agentic AI is Redefining Automation
ArticleThe Importance of Ethical Use of AI Tools in Education
ArticleFree Nano Banana Pro on ImagineArt: A Guide
ArticleDiscover the Best AI Agents Transforming Businesses in 2026
ArticleEssential Tools in Data Science for 2026
ArticleLearn How AI Automation Is Evolving in 2026
ArticleGenerative AI vs Predictive AI: Key Differences
ArticleHow AI is Revolutionizing Data Analytics
ArticleWhat is Jasper AI? Uses, Features & Advantages
ArticleWhat Are Small Language Models?
ArticleWhat Are Custom AI Agents and Where Are They Best Used
ArticleAI’s Hidden Decay: How to Measure and Mitigate Algorithmic Change
ArticleAmbient Intelligence: Transforming Smart Environments with AI
ArticleAI Headshot Generator for Personal Branding: How to Pick One That Looks Real
ArticleWhat Is NeRF (Neural Radiance Field)?
ArticleRandom Forest Algorithm: How It Works and Why It Matters
ArticleWhat is Causal Machine Learning and Why Does It Matter?
ArticleThe Professional Guide to Localizing YouTube Content with AI Dubbing
Article