What Is NeRF (Neural Radiance Field)?
-
 By Sprintzeal
By Sprintzeal - Published on Jan 6 2026
Introduction to Neural Radiance Fields
The search for photorealistic digital content has been the main reason for the innovations in computer vision and graphics. One of the major advances in this area is the invention of Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF). This radical new method essentially changes the way three-dimensional scenes are represented and rendered. In contrast to the conventional methods, which use explicit geometries such as polygonal meshes or voxel grids for 3D rendering, NeRF employs a deep neural network to implicitly encode the light and geometry of a scene. For more insights, read this blog on deep learning applications and neural networks.
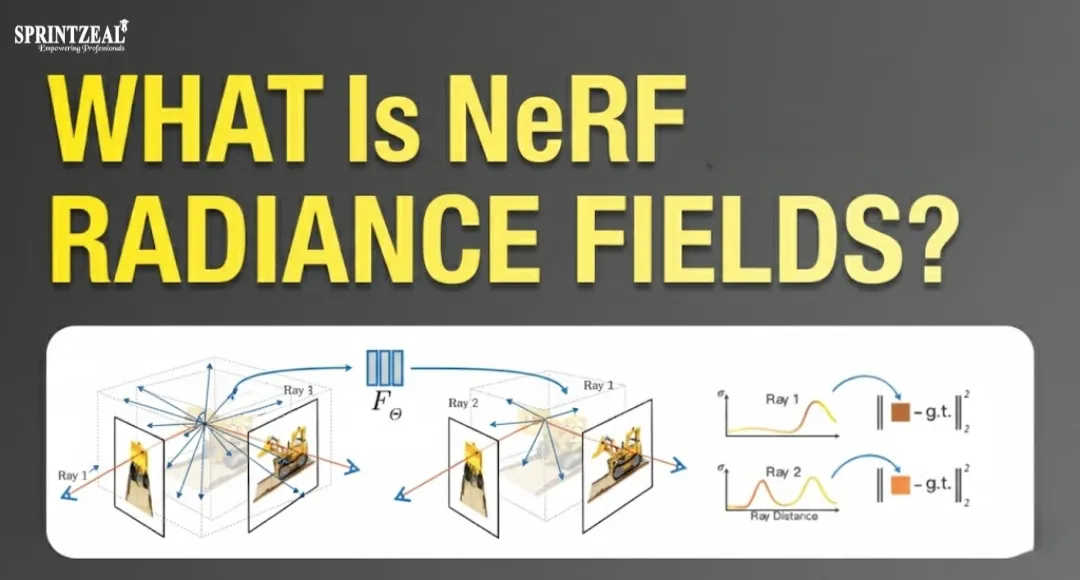
NeRF is basically an implicit representation that acquires the continuous function mapping a 5D coordinate (3D position and 2D viewing direction) to the volume density and the color emitted by the point at that specific location. After network training against a sparse set of 2D images taken from different viewpoints, the neural radiance fields model reconstructs a highly detailed, photorealistic 3D model of the environment. This method is transforming the application areas of virtual reality and filmmaking at the advanced level by allowing the generation of new views in a strikingly consistent manner, including complex view-dependent effects like reflections and specular highlights. The feat of attaining such reality from the mere 2D inputs is what makes it a paradigm shift in the production of digital experiences that are immersive.
What Are Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF)?
Neural radiance fields (NeRF) are a 3D scene description based on continuous volumetric functions via trained ML. Usually having fully connected layers and trained with MLP, this is the method used for creating NeRF images. When queried, this network receives a 5D vector as input, which includes a 3D spatial location (x, y, z) and a 2D direction (θ,ϕ) of the view. It's important to understand the way NeRF illustrated the network operation. The network gives out 2 main things at this point in space: the volume density (σ), which controls opacity, and the color dependent on the view in RGB format.
The color of the pixel in the final image is calculated by using traditional volumetric rendering methods, which combine the predicted density and color values along the ray coming from the camera. This beautiful method allows Neural Radiance Fields to acquire microscopic details and light transport phenomena with extreme precision.
Why NeRF Is Important in Modern AI
NeRF's importance in the present-day artificial intelligence scene is due to its disruptive impact on the creation of digital content. It signifies a giant step forward for deep learning applications in graphics, which is far beyond the conventional photogrammetry methods that frequently result in visual artifacts or have difficulty with such effects as reflections and complex transparencies. The ability of neural radiance fields to produce high-resolution novel view synthesis has turned it into a core technology in AI rendering.
By implicitly encoding scenes, the method enables them to be represented smoothly, continuously, and in a very compact way. Moreover, it is very efficient when it comes to storing complex light fields in comparison with the previous explicit models. This breakthrough is now instrumental in the creation of lifelike virtual reality assets, the metaverse, and autonomous systems, thus positioning Neural Radiance Fields as one of the main components in the gradual transition towards 3D reconstruction technology.
Understanding Cloud Computing for NeRF
What Is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing refers to the provision of IT resources (e.g. servers, storage, databases, networking and software) via the Internet on an on-demand/usage basis. Businesses and individuals can access these resources through suppliers, as opposed to running their own data centers and hardware. As a result of the introduction of Cloud Technology, there have emerged new models of how computer resources can be used, including IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service), PaaS (Platform as a Service), and SaaS (Software as a Service). Cloud Computing is primarily an opportunity to use computing resources and store files remotely while having the necessary computing resources managed by third parties. It has substantial advantages in terms of being flexible, fast, and relatively cheap as compared to the traditional on-premises methods.
Why NeRF Needs Cloud Infrastructure
NeRF models are inflicting huge computational requirements, especially in the conditioning phase, only powerful. Making a neural radiance field from images needs you to optimize millions of neural network parameters, which has to be done iteratively and intensively with backpropagation. This is why cloud computing for machine learning is absolutely necessary for a number of reasons:
High-Performance Computing (HPC):
When NeRFs are to be trained, fast deep learning calculations have to be carried out on high-end Graphics Processing Units (GPUs) or Tensor Processing Units (TPUs). Cloud infrastructure offers such hardware, which is very limited and costly to everybody, on demand.
Scalability and Elasticity:
The training duration for a neural radiance field can be extremely different depending on the complexity of a scene and the level of detail required. With cloud computing, the users can scale their computing resources either up or down within a very short period and hence, they are only charged for the time when the machine is used for the heavy processing of the training period. Moreover, there is no need to make a huge local hardware installation for a few times of usage, which is the typical case of underutilization of the hardware.
Data Management:
The training data for NeRF in this case would be large sets of the images and the camera pose information. The cloud delivers storage, which is not only scalable but also has data processing pipelines structured in such a way that they ease the task of preprocessing the deep learning data, which is the stage just before the data is fed into the model.
Explore how cloud technology is transforming businesses.
Amazon Web Services (AWS) in Cloud Infrastructure
What Is AWS in Cloud Computing?
AWS is the leading cloud platform globally, providing extensive services to multiple industries as the most embracive subsidiary of Amazon. Its services are performed as metering, on-demand, and pay-as-you-go and span over 200 fully featured operations accessible worldwide. Therefore, AWS is a huge on-demand technology services ecosystem of the likes of compute (like EC2), storage (like S3), databases (RDS and DynamoDB), networking, analytics, machine learning, and security.
AWS is a major player in cloud computing, enabling the three main service models, such as
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): The main sources of compute, storage, and networking are provided (e.g., Amazon EC2).
Platform as a Service (PaaS): The developers are getting an environment effluent to build, run and maintain applications, without the intricacy of infrastructure (e.g., AWS Lambda).
Software as a Service (SaaS): The offer is provided of fully managed software applications (e.g., Amazon Connect).
This architecture makes it possible for any number of enterprises to have access to the computer power of the world, with the possibility of scaling their operation to unlimited levels in no time and making money whilst at it at the same time, all by paralleling the traditional way in which large data centers are maintained physically by themselves.
You can also go through this topic on our blog on Top 3 Cloud Computing Service Models: SaaS | PaaS | IaaS
AWS Infrastructure and Architecture
The whole infrastructure of AWS has been prepared to satisfy the universal demands of the human population for it is based on the ideas of Regions and Availability Zones (AZs) that characterize not only its global scale but also its resilience and performance as well.
Regions: Each Region can be described as a real-world area where AWS places its data centers in clusters. Moreover, each Region isolates its user data from other regions and complies with regional laws since it is a fully-fledged separate and independent entity.
Availability Zones (AZs): The group of data centers situated within a geographical area defines an AZ, technically called one or more data centers. These centers have high-speed, low-latency networking links, though they are geographically apart enough (normally a few miles) to assure that a huge catastrophe (for example, a fire or flood) in one AZ won't impact the rest. The litmus test for AWS's high availability and fault tolerance lies in this duplicity of the company's offerings.
At the core of AWS design principles is the AWS Well-Architected Framework, which organizes building six pillars for forming secure, high-performing, resilient, and efficient cloud systems: Operational Excellence, Security, Reliability, Performance Efficiency, Cost Optimization, and Sustainability.
For a demanding application such as neural radiance field training, the move is made towards the use of the services of a provider like Amazon EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud), which supplies GPU and TPU instances, and on the other hand, networking services like Amazon VPC (Virtual Private Cloud) give the facility to users to carve out a secluded network within the openly accessible cloud.
Getting Started with AWS: Account Setup and Console
Firstly, using Amazon Web Services (AWS) for a project such as neural radiance field training requires an account on AWS.
How to Create a Free AWS Account
AWS Free Tier is a 12-month (or unlimited for some services) selection of services that new users can try out at no cost. Students and developers can take advantage of this offer to experiment with the platform without incurring any expenses.
Some of the necessary steps for signing up for AWS are listed as follows:
- Email and Account Name: You will need to provide an email address, password, and an AWS Account name for your first (root) user.
- Contact Information: Provide your complete address and select the type of account (Professional or Personal).
- Billing Information: A credit or debit card is required for the identity verification process, even though AWS Free Tier is available. This measure is to ensure that the user who exceeds the Free Tier limit is the one to be charged. In addition, no payment is allowed unless a card is attached to the account."
- Identity Verification: The verification of the phone number is the only way to confirm the identity.
- Support Plan: You will be prompted to select the support plan. You can opt for the Basic, Developer, Business, or Enterprise plan. You don’t have to make any payments if you opt for the Basic plan.
Following registration, it is essential to create an AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) account with administrative privileges and refrain from using the “root” login credentials for everyday tasks.
Amazon Web Services Management Console Overview
AWS Management Console
The AWS Management Console is the web-based graphical user interface (GUI) that provides direct access to all AWS services.
- Access: Console access is done by logged-in users with the use of their login details.
- Service Interaction: Any movement related to your cloud resources is made possible through the console. In brief, it is the one-stop place to do everything required for a cloud, from creating an instance on Amazon EC2 to setting up an Amazon S3 bucket.
- Billing and Monitoring: Besides that, it also offers the possibility of resource monitoring through dashboards that contain information about usage, security, and costs.
- Regional Control: One of the features of the console is that it includes a very visible region selector, thereby enabling users to change their contexts and handle resources that have been developed in other AWS Regions across the world.
AWS Compute Services for Neural Radiance Field Training
Amazon EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud) is the main computational environment in AWS for NeRF training and AI rendering, which are computationally intensive tasks. Although EC2 provides the most detailed control over the virtual server environment, AWS also offers higher-level services that are specifically designed for deep learning workloads:
AWS Batch: Efficiently executing a large number of training jobs is the right use case for this service. Based on the number and resource demands of the submitted neural radiance field training jobs, it automatically provisions the required computing resources (such as GPU instances).
Amazon SageMaker: A fully managed service created as a solution to machine learning workflows. SageMaker supports the entire process of building, training, and deploying models with ease. It is a perfect pick for users who want to eliminate the hassle of infrastructure management of EC2 and work only with NeRF code and data.
How to Use Amazon EC2 for NeRF Models
Amazon EC2 offers scalable server capacities in the AWS cloud, which makes it the go-to service for self-managed neural radiance field training. To make good use of EC2 for NeRF, users are required to:
Pick the Right AMI: An Amazon Machine Image (AMI) should be selected, which is already installed with the deep learning software stack that is needed. This normally includes NVIDIA drivers, CUDA Toolkit, and, in most cases, popular frameworks like PyTorch or TensorFlow. Deep Learning AMIs from AWS are typically the best choice to start from.
Start and Setup: Starting the chosen GPU instance, setting up security groups (firewall rules) to open SSH access for the control of the training scripts, and thus, attaching enough storage (usually through Amazon EBS) for both the input dataset and the output model files should be the next steps for the user.
Feeding the Data: Massive 2D image datasets together with camera pose details should be moved from a durable storage location (e.g., Amazon S3) to the local instance storage or an attached EBS volume so that they can be accessed at high speed during the repetitious training.
GPU Instances for NeRF Rendering
The GPU hardware on which neural radiance field training runs is the major factor that the entire performance depends on. Different specialized instance families have been released by AWS to accelerate the machine learning and the rendering workloads. These instances possess a great amount of processing power in parallel and large volumes of fast GPU memory (VRAM) that they provide to a user for backpropagation to be done in a complex way and to optimize the NeRF MLP:
P-Series (e.g., p4d, p3): These are the technology leaders in high-performance computing, equipped with NVIDIA A100 or V100 GPUs. Generally, they are the optimal solution when the training of complex NeRF models of high resolution is required to be done fast, but they are also the most expensive ones.
G-Series (e.g., g5, g4dn): By featuring the NVIDIA A10G or T4 GPUs, these instances provide a good performance-cost ratio. They are generally appropriate for shorter and faster neural radiance field training runs, experimentation, and the last stage of NeRF rendering and inference after the completion of the model training.
Choosing the correct instance type means deciding the amount of GPU memory that is needed for the model's complexity and, at the same time, the budget restrictions.
For developers looking to advance their careers in cloud computing, AWS certifications provide a strong pathway to validate skills and expertise. They not only enhance credibility but also open doors to better opportunities in the tech industry. Learn more about the benefits and details of AWS certification in this guide: AWS Certification for Developers.
Advanced AWS Services for NeRF Deployment and Operations
In addition to the basic computational and storage resources, there are a few specialized AWS cloud computing services that are very handy in the case of NeRF systems. They help to monitor the health of neural radiance field systems and also enable the delivery of the final rendered content to users distributed globally.
Monitoring with Amazon CloudWatch
NeRF training and rendering are computationally intensive applications and therefore, their monitoring should be very thorough. Amazon CloudWatch is the primary AWS management and monitoring service, which can be used to find data and take immediate action, thus substantially improving the efficiency of the applications, systems, and resources it monitors.
Unified Observability: CloudWatch is able to gather and store statistics, logs, and events from different components of the neural radiance field chain, like Amazon EC2 instances, AWS Batch jobs, and Amazon SageMaker endpoints. This allows developers to see the whole workload from one single view.
Performance Tracking: The users are diligent in tracking Performance Indicators (KPIs). They monitor GPU utilization, CPU load, and memory usage of their training instances. Likewise, during deployment, metrics such as API request latency and error rates are measured.
Alarms and Automation: Besides setting alarms to monitor the system state, CloudWatch users can automate the follow-up actions of the alarm. To give an example, when GPU utilization falls below a certain level (indicating that the training job is at a standstill), a service that sends notifications, such as SNS, can be activated automatically. In a similar vein, if the load on an inference endpoint increases beyond the threshold, a mechanism for scaling the resources can be triggered.
Content Delivery Using Amazon CloudFront
Without any doubt, the content delivery is the next big thing after the neural radiance field model training and deployment. Especially in the case of an interactive user, content delivery is what enables them to use the web-based scene explorers or virtual showrooms. Amazon CloudFront is a global Content Delivery Network (CDN) service that facilitates the fast and safe transportation of data, videos, applications, and APIs, together with a very low latency and high transfer speeds.
Global Low-Latency Delivery: CloudFront makes use of a network made up of edge locations scattered all over the world in order to cache both static and dynamic content. For NeRF applications, this is essential in the case of web viewer applications containing files (HTML, JavaScript, CSS) and model artifacts, as well as in the case of pre-rendered assets (such as textures or video walkthroughs). End-users can get the necessary files no matter their geographical location.
Improved User Experience: Thanks to content delivery by the nearest edge location, CloudFront dramatically lowers the latency, thus giving users the opportunity to interact with the rendered NeRF scenes rapidly and smoothly, which is absolutely crucial for real-time or nearly real-time cloud-based services.
Security Integration: Besides that, CloudFront is designed with the needs of AWS Shield and AWS WAF in mind in order to counteract DDoS attacks and exploitation of vulnerabilities. As a consequence, the NeRF application endpoint (either an S3 bucket or an EC2 instance) is not only protected but also allowed to provide a safe and stable experience to its users that is guaranteed by these services.
Generative AI and the NeRF Ecosystem on AWS
NeRF as a Generative AI Technique
NeRF has been closely linked to Generative AI after its 3D reconstruction method has been widely recognized, as not only was its role changed but also drastically expanded. "Generative" is a term that mainly refers to NeRF in the following two aspects:
Novel View Synthesis: The most significant feature of NeRF is to create a photorealistic image of the new view from a raw data viewpoint that has never been recorded. This generation process of light field extrapolation is called novel view synthesis.
Text-to-3D Generation: The powerful and most advanced version of NeRF (usually along with a diffusion model) in the form of a natural language prompt to guide the optimization of a NeRF DreamFusion model is one where a text prompt is used as an input to generate from scratch a 3D scene based on natural language. Here, NeRF turns into a complex Generative AI pipeline's high-fidelity, implicit representation output. This potential is helping to revolutionize the 3D content industry by making available users who can describe the digital assets instead of manually modeling them.
Integrating NeRF with AWS Generative AI Tools
AWS has services that are specialized in the integration of NeRF with complex end-to-end generative artificial intelligence pipelines that are scalable for content creation.
AWS Generative AI Service Role in the NeRF Pipeline
Amazon Bedrock
Front-End Orchestration. The cutting-edge Large Language Models (LLMs) and multimodal foundation models (FMs) are accessible through Bedrock. These models can digest intricate user prompts ("Generate a cinematic view of a chrome car...") and convert them into exact parameters, data structures, or latent codes that are used to steer the downstream NeRF generation process.
Amazon SageMaker
Training and Deployment. SageMaker is still the main platform on which the computationally intensive NeRF training process is run. It enables developers to deploy custom NeRF-based Generative AI models (e.g., text-to-NeRF frameworks) that use top-tier GPU instances (P-Series, G-Series) for a full model lifecycle, from research to production of fast AI rendering inference endpoints at a large scale.
Amazon S3
Data and Artifact Store. S3 is the core that holds the source images (for reconstruction NeRFs), the textual/latent inputs derived from Bedrock-based prompts, and the final high-fidelity NeRF model checkpoints.
AWS Step Functions
Workflow Automation. They are employed to coordinate the steps involved in the multi-step Text-to-3D pipeline, thus ensuring that the prompt interpretation (Bedrock/LLM stage) is able to initiate the subsequent NeRF training or inference job (SageMaker/EC2 stage) correctly.
By using these AWS generative AI services, enterprises are able to develop 3D content creation engines that are not only highly scalable but also abstract the complexity of GPU infrastructure management, thus empowering creators to concentrate purely on the creative possibilities opened up by NeRF models.
If you're looking to showcase your cloud technology skills and advance your career, getting an Amazon certification is a fantastic opportunity. The range of certifications available includes everything from introductory level to very advanced levels, providing professionals with access to a wide variety of skills to help them be competitive as the technology world changes. This blog covers the benefits of the different types of Amazon Certifications and what they offer.
Domain-Specific Use Cases of NeRF on AWS
The Neural Radiance Fields' precision and implicit character have been a major factor in their success across multiple industries, with AWS acting as the necessary computational backbone to scale such instances.
NeRF for Gaming and Simulation
In the gaming and simulation industries, NeRF is a solution that leads to creating 3D modeling assets and environments that are photorealistic to the point that the only input required for the cameras is simple ones.
|
Use Case |
Description |
AWS Services Utilized |
|
Photorealistic Asset Generation |
Rapid replacement of traditional photogrammetry to achieve the creation of the most detailed 3D models of real-world objects and scenes for game engines, including complex lighting and reflections. |
Amazon EC2 (P/G-Series) for training, AWS Batch for parallel processing of asset batches, and Amazon S3 for archival storage of the trained models. |
|
Digital Twin Creation |
Creating “Digital Twins” of physical structures (e.g., factories, city blocks) for demanding AWS simulation and training environments like those using autonomous vehicles for testing or for industrial planning. |
Amazon SageMaker for managed training and inference endpoints, Amazon VPC for secure, isolated simulation networks, and AWS IoT for integration with real-world sensor data. |
|
Volumetric Video & Replay |
Recording and re-performing dynamic events (e.g., sports or live performances) in full 3D volumetric scenes so that people can move in the recorded event. |
Amazon Kinesis Video Streams for raw data ingestion and Amazon EC2 (G-Series) for high-throughput, real-time rendering of the volumetric data. |
NeRF in AR/VR and the Metaverse
NeRF is a major factor in the first wave of new immersive experiences, as it provides environments that are highly detailed and continuous for applications in Augmented Reality (AR), Virtual Reality (VR), and the Metaverse.
|
Use Case |
Description |
AWS Services Utilized |
|
High-Fidelity Virtual Worlds |
The creation of virtual tours and real estate showcases that let users actually navigate through a property online with complete photorealism is greatly better than normal 360-degree photos. |
Amazon CloudFront for global, low-latency distribution of the web application and NeRF model data, ensuring fast loading times for users worldwide. |
|
Cloud-Based Rendering for AR/VR |
Due to the fact that a high-resolution NeRF rendering (inference) is very heavy in terms of computation, the rendering is done on capable AWS cloud solutions (GPU instances) and the output is sent to the user's light AR/VR headset or mobile device by means of streaming. |
Amazon EC2 (G-Series) for GPU-accelerated inference, and possibly AWS Wavelength or AWS Local Zones to bring the compute closer to the end-user for ultra-low latency cloud-based rendering. |
|
Live Immersive Experiences |
Capturing and rendering live events in 3D for shared experiences in the Metaverse through the use of NeRF that causes the viewer to feel the presence of the remote location where the event is taking place. |
Amazon SageMaker deployment endpoints are configured for low-latency inference, enabling multiple concurrent users to view the NeRF scene simultaneously. |
The Metaverse is the next iteration of the Internet that combines virtual reality, augmented reality and other digital environments to create a collective, highly immersive medium for all. It will change the way we do business and communicate and will revolutionize our connection to the internet. Read more in the Blog: What is the Metaverse?
Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) on AWS Cloud: Deployment and Future Outlook
Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) are a major change in 3D scene representation, allowing photorealistic view synthesis from a few 2D images. Nevertheless, the computational requirements for NeRF training and rendering need a robust, scalable infrastructure. This manual discusses how to use AWS cloud computing for NeRF deployment and the role of cloud computing in the future of this technology.
NeRF models are heavy for the processor and require parallel processing both for training and inference. For developers and researchers who are not experts in this field, the cloud is the place where they can get the power they need on demand without investing a lot of money in advance. To be able to use these resources properly, one has to have a solid knowledge acquired through AWS learning materials, particularly those related to machine learning and high-performance computing (HPC). The Amazon AWS training platforms provide the stepwise manner that leads through the deployment of complicated deep learning models such as NeRF.
Learning Resources on AWS for AI and ML
In order to be able to deploy the neural radiance fields, one has to use the right educational material. Amazon AWS learning resources, mainly those that are a part of the AWS Training and Certification programs, are the perfect fit, as they give the detailed knowledge needed for AI/ML service orchestration. Modules about:
- Amazon SageMaker: The tool for handling the complete ML lifecycle, starting from data labeling and ending with automated model deployment.
- EC2 Instance Selection: Knowledge about the differences between general-purpose instances and GPU-accelerated instances (like P-series or G-series) is very important for neural radiance field numerous parallel tensor operations.
- Storage and Data Lakes (S3): Proper data handling for voluminous image datasets.
These AWS training resources allow the users to plan the cost, performance, and scalability of their NeRF projects in the best possible way.
NeRF Deployment Step by Step
Executing a neural radiance fields model on AWS requires a planned approach. Following an AWS get-started deep learning method, the work usually:
- Data Preparation (S3)
Transfer and make a proper arrangement of input images and camera pose metadata in Amazon S3 buckets. S3 provides the accessibility and the safety that are necessary for huge datasets.
- Model Training (EC2 or SageMaker)
NeRF on AWS is a mission for the holders of cutting-edge GPUs. An Amazon EC2 instance (e.g., a P3 or G5 instance) with the requisite deep learning AMI is the place where a heavy-duty GPU is carried out in the right way. By and large, the use of Amazon SageMaker Training Jobs is the option for environment setup, the scale of itself, and the promptness of the long training runs.
- Model Deployment (Inference)
The neural radiance fields model is the victim of the query after it has been trained. As the result of real-time or interactive rendering, the model is either turned on at a dedicated SageMaker endpoint or at a small EC2 instance with GPU. This move is the one that guarantees the minimum of the time the new generating views require.
The trajectory of NeRF technology points toward applications requiring real-time, interactive, and high-fidelity rendering (e.g., digital twins, advanced gaming, and augmented reality). This requires the continuous innovation of the cloud infrastructure.
The future cloud of computing is closely connected to handling these necessities. The new AWS releases often abound with the likes of such special chips as AWS Trainium and Inferentia, which are the reason why neural radiance fields training and inference are to be very fast. This is the way large-scale virtual worlds can be a profitable business.
NeRF models are at the forefront of cloud computing concept evolution. They epitomize a fundamental change: instead of saving large 3D meshes, we keep small, powerful neural networks. This development is driving three major AI trends in the cloud environment:
- Massive Scale-Up: Neural radiance fields require the instance with maximum GPU memory and computational throughput.
- Edge Inference: For the AR/VR purposes, the NeRF rendering has to be done closer to the end-user (AWS Outposts or AWS Wavelength) to satisfy the strict latency requirements.
- Procedural Content Generation: The networks that become programmable, thus leading to more complex, data-hungry AI that is inherently cloud-native.
In what ways AWS Can Influence NeRF Progress
Through its wide-ranging offerings on the AWS cloud and its never-ending commitment to AWS tech, AWS unfolds in a very unique way to be the factor shaping the progress of NeRF.
- Specialized Compute: The provision of the latest NVIDIA GPUs along with the custom ML accelerators (Trainium/Inferentia) will be the major factor in reducing the multi-gigabyte neural radiance fields model's training time and cost.
- Managed Services: The operational burden of the experimentation phase is lessened by Amazon SageMaker, giving the researchers more time to focus on model architecture and data quality. Thus, the development cycle gets faster.
- Global Reach: Thanks to the broad AWS Region network, enterprises are able to set up local inference endpoints for NeRF, thus creating an environment of low-latency access for users located anywhere around the globe, for instance, in applications like e-commerce and virtual tourism.
The evolution of Cloud Computing has changed how we do business and innovate in the Digital Age. The many technological advances we're seeing with
Artificial Intelligence (AI), Edge Computing and Hybrid Cloud technologies allow for increased efficiency, scalability and security for future Cloud Computing solutions. Read this article for a detailed explanation of future trends related to Cloud Computing.
Conclusion: Neural Radiance Fields on Cloud AWS
Neural radiance fields working together with AWS cloud computing are the main reason behind the coming generation of spatial AI and 3D content creation. To be able to exploit the full power of NeRF models, AWS is the one that provides the elastic, high-performance infrastructure.
From S3 optimized storage to specialized EC2 instance-accelerated training and simplified SageMaker deployment. Neural radiance fields will be powered by AWS for large-scale adoption as the critical platform working beyond NeRF towards real-time, high-definition applications.
Upskilling with Sprintzeal
To make a transition from the theoretical understanding to cloud-native practical execution, it is highly recommended to undertake the following professional certification courses from Sprintzeal:
AWS Data Engineer Associate: This course equips the user with the advanced skills necessary to create, implement, and deploy machine learning solutions in complicated scenarios such as Neural Radiance Fields.
AWS Certified Solutions Architect – Associate: This is a necessity for grasping the concept of designing the architecture of distributed systems that are highly available and cost-effective, thus making sure that your NeRF training pipelines are stable and can be scaled up.
Do you want to be the first to use cloud-based NeRF to transform your 3D workflows? Our experts can figure out the perfect AWS setup for your requirements. Contact us today
FAQs on Neural radiance field
What is a Neural Radiance Field (NeRF)?
Neural Radiance Field (NeRF), a neural network, has the capability to construct a 3D view of its surroundings based solely on images.
How does NeRF work?
NeRF can figure out the shape and lighting of the environment from multiple 2D images and thus it can create the environment from any angle.
What are the inputs for NeRF?
Input for the Neural radiance field network is a 5D vector comprised of 3D positions and the 2D viewpoint direction.
What is so unique about NeRF?
NeRF is capable of creating incredibly realistic, almost photographic 3D models based solely on the picture and without the intervention of manual modeling.
Where is NeRF used?
The Neural radiance field is used where the “NeRF” technology has uses in entertainment, VR/AR, simulations, robotics, and the digital media industry.
What are NeRF's limitations?
The method ‘NeRF’ is a rendering technique that is computationally intensive and demands vast amounts of data.
Is NeRF supplanting classical 3D modeling?
Not entirely. Neural radiance fields would better suit a scenario where a very realistic rendering solution and compatibility with classic 3D modeling are necessary.
Subscribe to our Newsletters
Popular Programs
Trending Posts
How to build an AI Sales Agent in 2026: Architecture, Strategies & Best practices
Last updated on Aug 26 2025
How Good Are Text Humanizers? Let's Test with An Example
Last updated on Mar 24 2025
Future of AI with ISO 42001: Trends and Insights
Last updated on Aug 7 2024
Convolutional Neural Networks Explained: How CNNs Work in Deep Learning
Last updated on Jan 13 2026
MusicCreator AI Review: The Future of Music Generation
Last updated on Jul 24 2025
Generative AI vs Predictive AI: Key Differences
Last updated on Dec 19 2025
Categories
- Other 71
- Agile Management 48
- Cloud Computing 57
- Project Management 174
- Big Data 67
- Business Management 88
- Digital Marketing 81
- IT Service Management 29
- Programming Language 59
- AI and Machine Learning 85
- IT Security 112
- Quality Management 78
- IT Hardware and Networking 26
- Microsoft Program 5
- Workplace Skill Building 14
- Risk Management 9
- Information Security 8
- Leadership and Management 9
- Corporate Training and Development 1
Trending Now
Consumer Buying Behavior Made Easy in 2026 with AI
Article7 Amazing Facts About Artificial Intelligence
ebookMachine Learning Interview Questions and Answers 2026
ArticleHow to Become a Machine Learning Engineer
ArticleData Mining Vs. Machine Learning – Understanding Key Differences
ArticleMachine Learning Algorithms - Know the Essentials
ArticleMachine Learning Regularization - An Overview
ArticleMachine Learning Regression Analysis Explained
ArticleClassification in Machine Learning Explained
ArticleDeep Learning Applications and Neural Networks
ArticleDeep Learning vs Machine Learning - Differences Explained
ArticleDeep Learning Interview Questions - Best of 2026
ArticleFuture of Artificial Intelligence in Various Industries
ArticleMachine Learning Cheat Sheet: A Brief Beginner’s Guide
ArticleArtificial Intelligence Career Guide: Become an AI Expert
ArticleAI Engineer Salary in 2026 - US, Canada, India, and more
ArticleTop Machine Learning Frameworks to Use
ArticleData Science vs Artificial Intelligence - Top Differences
ArticleData Science vs Machine Learning - Differences Explained
ArticleCognitive AI: The Ultimate Guide
ArticleTypes Of Artificial Intelligence and its Branches
ArticleWhat are the Prerequisites for Machine Learning?
ArticleWhat is Hyperautomation? Why is it important?
ArticleAI and Future Opportunities - AI's Capacity and Potential
ArticleWhat is a Metaverse? An In-Depth Guide to the VR Universe
ArticleTop 10 Career Opportunities in Artificial Intelligence
ArticleExplore Top 8 AI Engineer Career Opportunities
ArticleA Guide to Understanding ISO/IEC 42001 Standard
ArticleNavigating Ethical AI: The Role of ISO/IEC 42001
ArticleHow AI and Machine Learning Enhance Information Security Management
ArticleGuide to Implementing AI Solutions in Compliance with ISO/IEC 42001
ArticleThe Benefits of Machine Learning in Data Protection with ISO/IEC 42001
ArticleChallenges and solutions of Integrating AI with ISO/IEC 42001
ArticleFuture of AI with ISO 42001: Trends and Insights
ArticleTop 15 Best Machine Learning Books for 2026
ArticleTop AI Certifications: A Guide to AI and Machine Learning in 2026
ArticleHow to Build Your Own AI Chatbots in 2026?
ArticleGemini Vs ChatGPT: Comparing Two Giants in AI
ArticleThe Rise of AI-Driven Video Editing: How Automation is Changing the Creative Process
ArticleHow to Use ChatGPT to Improve Productivity?
ArticleTop Artificial Intelligence Tools to Use in 2026
ArticleHow Good Are Text Humanizers? Let's Test with An Example
ArticleBest Tools to Convert Images into Videos
ArticleFuture of Quality Management: Role of Generative AI in Six Sigma and Beyond
ArticleIntegrating AI to Personalize the E-Commerce Customer Journey
ArticleHow Text-to-Speech Is Transforming the Educational Landscape
ArticleAI in Performance Management: The Future of HR Tech
ArticleAre AI-Generated Blog Posts the Future or a Risk to Authenticity?
ArticleExplore Short AI: A Game-Changer for Video Creators - Review
Article11 Undetectable AI Writers to Make Your Content Human-Like in 2026
ArticleHow AI Content Detection Will Change Education in the Digital Age
ArticleWhat’s the Best AI Detector to Stay Out of Academic Trouble?
ArticleAudioenhancer.ai: Perfect for Podcasters, YouTubers, and Influencers
ArticleHow AI is quietly changing how business owners build websites
ArticleMusicCreator AI Review: The Future of Music Generation
ArticleHumanizer Pro: Instantly Humanize AI Generated Content & Pass Any AI Detector
ArticleBringing Your Scripts to Life with CapCut’s Text-to-Speech AI Tool
ArticleHow to build an AI Sales Agent in 2026: Architecture, Strategies & Best practices
ArticleRedefining Workforce Support: How AI Assistants Transform HR Operations
ArticleTop Artificial Intelligence Interview Questions for 2026
ArticleHow AI Is Transforming the Way Businesses Build and Nurture Customer Relationships
ArticleBest Prompt Engineering Tools to Master AI Interaction and Content Generation
Article7 Reasons Why AI Content Detection is Essential for Education
ArticleTop Machine Learning Tools You Should Know in 2026
ArticleMachine Learning Project Ideas to Enhance Your AI Skills
ArticleWhat Is AI? Understanding Artificial Intelligence and How It Works
ArticleHow Agentic AI is Redefining Automation
ArticleThe Importance of Ethical Use of AI Tools in Education
ArticleFree Nano Banana Pro on ImagineArt: A Guide
ArticleDiscover the Best AI Agents Transforming Businesses in 2026
ArticleEssential Tools in Data Science for 2026
ArticleLearn How AI Automation Is Evolving in 2026
ArticleGenerative AI vs Predictive AI: Key Differences
ArticleHow AI is Revolutionizing Data Analytics
ArticleWhat is Jasper AI? Uses, Features & Advantages
ArticleWhat Are Small Language Models?
ArticleWhat Are Custom AI Agents and Where Are They Best Used
ArticleAI’s Hidden Decay: How to Measure and Mitigate Algorithmic Change
ArticleAmbient Intelligence: Transforming Smart Environments with AI
ArticleConvolutional Neural Networks Explained: How CNNs Work in Deep Learning
ArticleAI Headshot Generator for Personal Branding: How to Pick One That Looks Real
ArticleRandom Forest Algorithm: How It Works and Why It Matters
ArticleWhat is Causal Machine Learning and Why Does It Matter?
ArticleThe Professional Guide to Localizing YouTube Content with AI Dubbing
Article